Space 101 | What Is Gravity? 
The Mysterious Force Of Attraction
Gravity is a type of force of attraction between two objects with mass. The force increases with the amount of mass and as the objects get closer. This is believed to be due to the way masses warp and distort the fabric of space according to Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity. Gravity keeps all objects in orbit, forms the Earth’s ocean tides and causes meteorites to fall to Earth!
What We Know About Gravity
Have you ever wondered why when you throw a ball or knock something off a table they fall to Earth? Or why when you run and jump, you can’t just fly off into space like Superman? Well, that’s all because of gravity!
Gravity is an invisible type of force which causes two objects with mass to be attracted to one another. And the closer they are, the greater the force between them. This doesn’t just include the force pulling you down to Earth’s surface, gravity acts on everything across the universe, big and small, even energy such as radio waves and light!
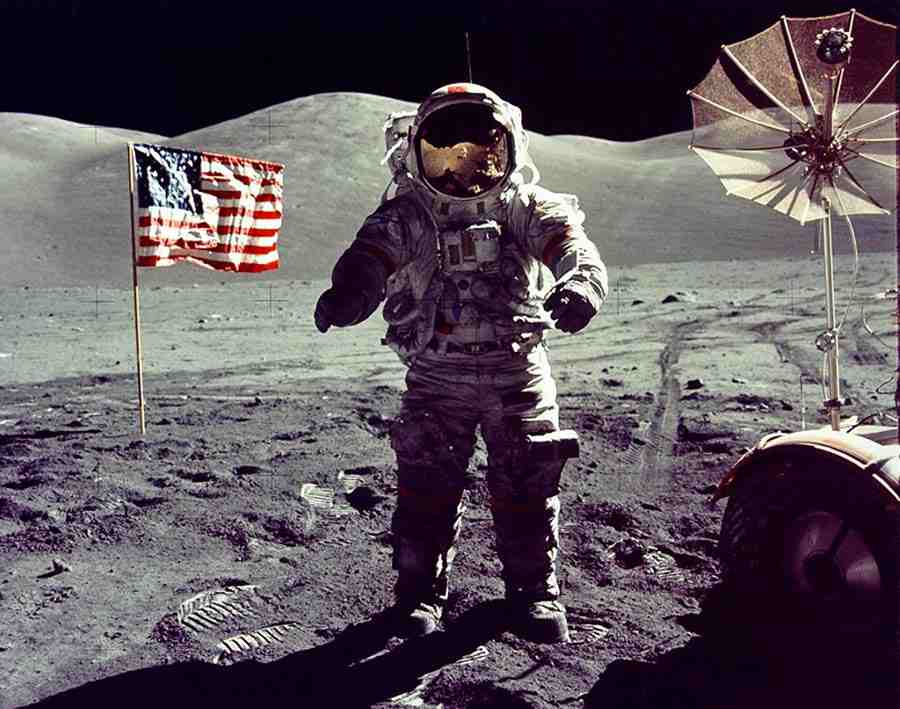
The more mass an object has, the greater its gravity is. It’s for this reason if you could stand on Jupiter’s surface, you would weigh 2 ½ times what you do on Earth! You would feel very heavy and struggle to even stand up! Alternatively, the Apollo astronauts experienced only 1/6th Earth’s gravity when standing on the Moon. This is because the Moon has less mass than the Earth.
Black holes are objects dominated by their extreme gravity. They have accumulated so much matter, into such a small volume, that nothing can escape their gravitational pull. Not even light!
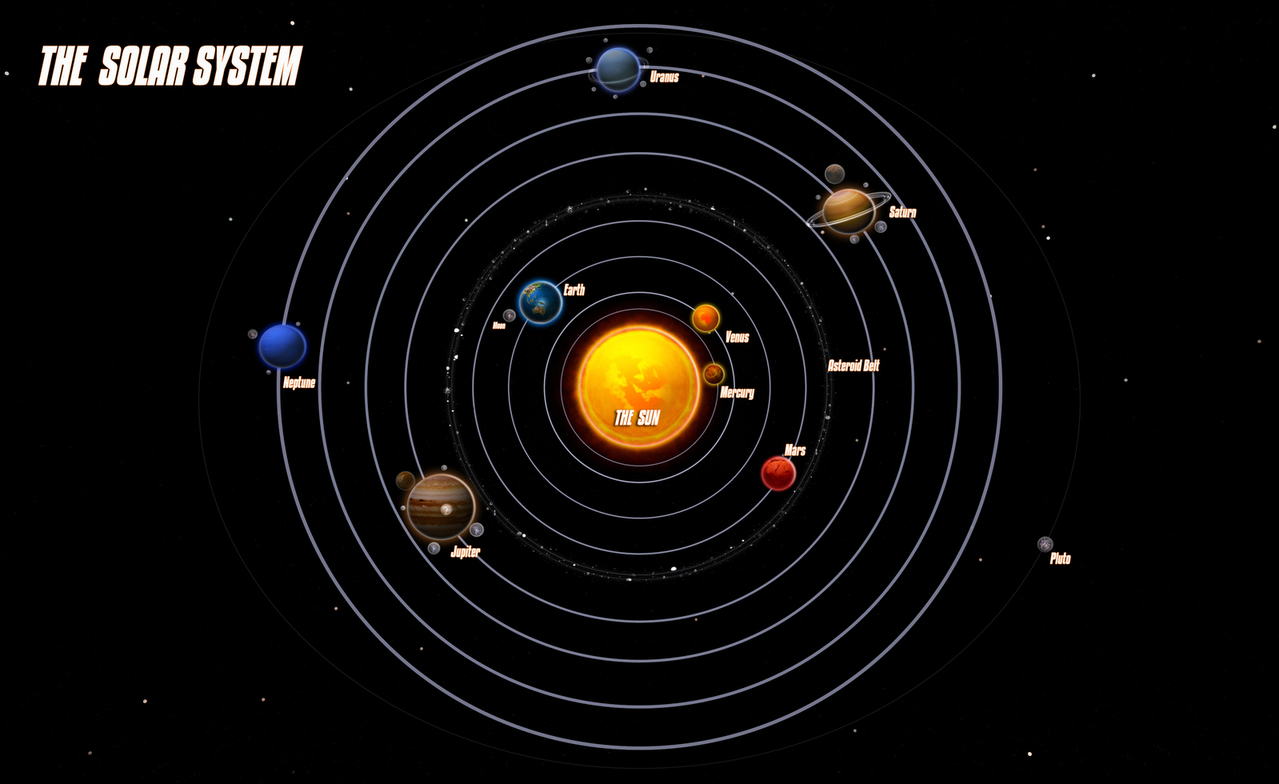
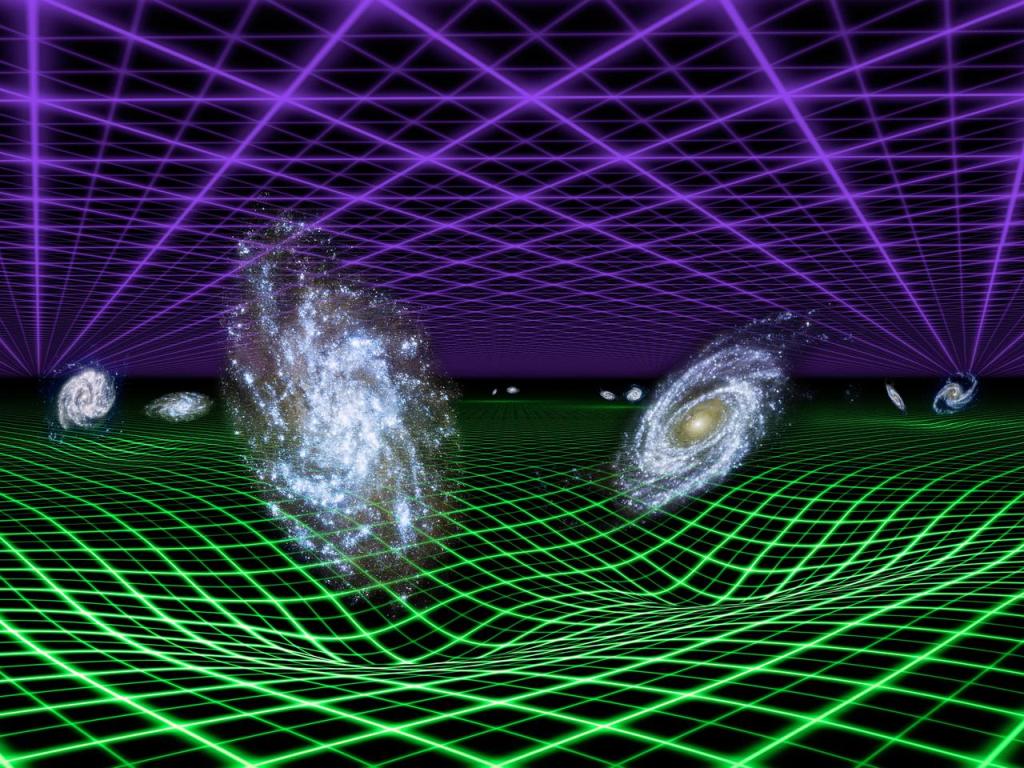
Gravity is responsible for collapsing clouds of gas (nebula), forming stars, the planets and ultimately galaxies. Gravity is the reason that the planets stay in orbit around the Sun. It’s the force that keeps the Moon in orbit around the Earth, preventing it from just flying off into space. At the same time, the Moons’ gravity causes Earth’s ocean tides.
Scientists still don’t fully understand how gravity works, but Sir Isaac Newton, after famously witnessing an apple fall to the ground, described gravity as the attraction of two bodies with mass. For centuries Newton’s equation describing the force of gravity as being relative to the masses of the bodies (with the force quickly decreasing with an increase in distance between them), was a good approximation.
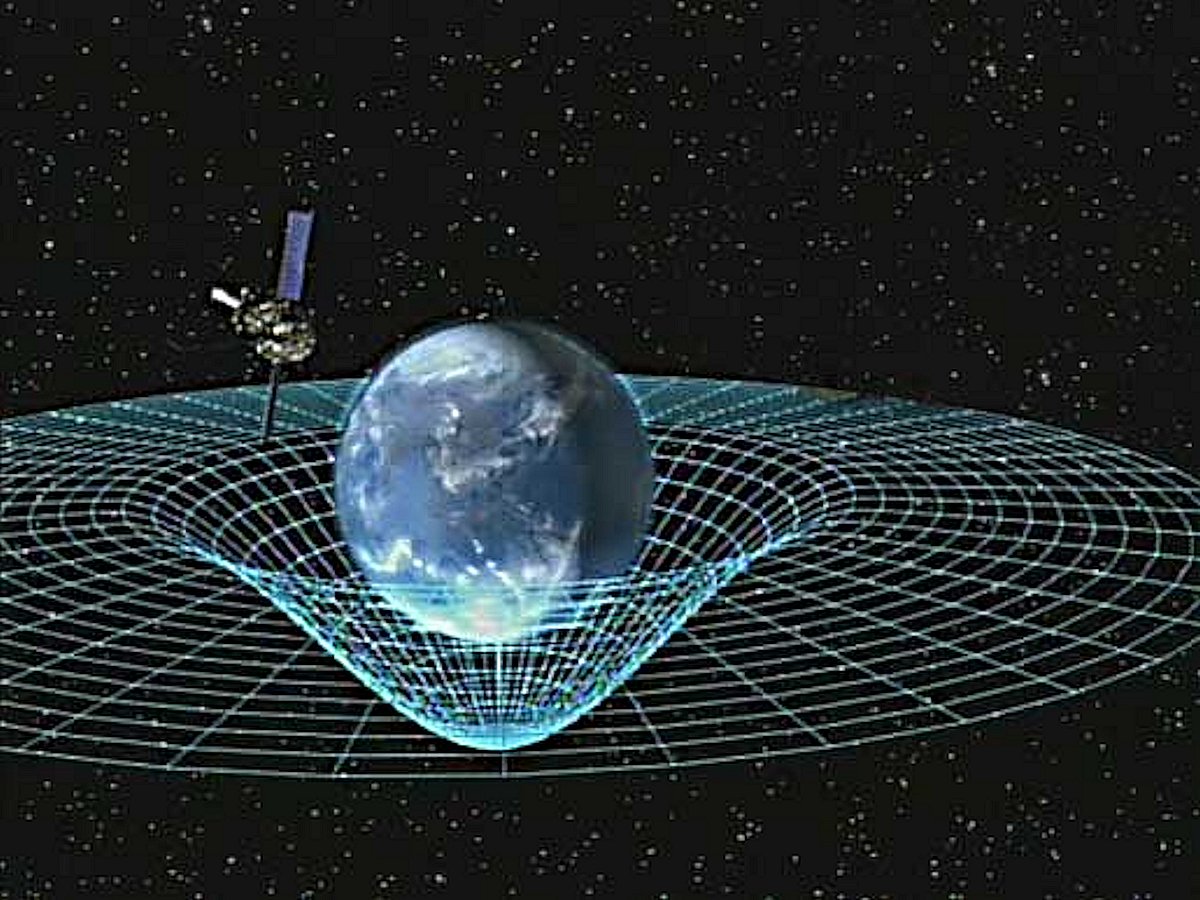
The most accurate description of gravity has been made by Albert Einstein’s brilliant General Theory of Relativity. Einstein describes gravity not as a force between two masses, but as the observed effect a large mass has on the fabric of space (called spacetime). The theory describes large masses curving and warping space, in a sense, creating slopes in space (or depressions) which objects ‘fall’ towards. This gives the appearance of a force of attraction!