Viking 1 & 2 | The Twin Martian Orbiter And Lander Spacecraft
Mars’ Trailblazing Twins
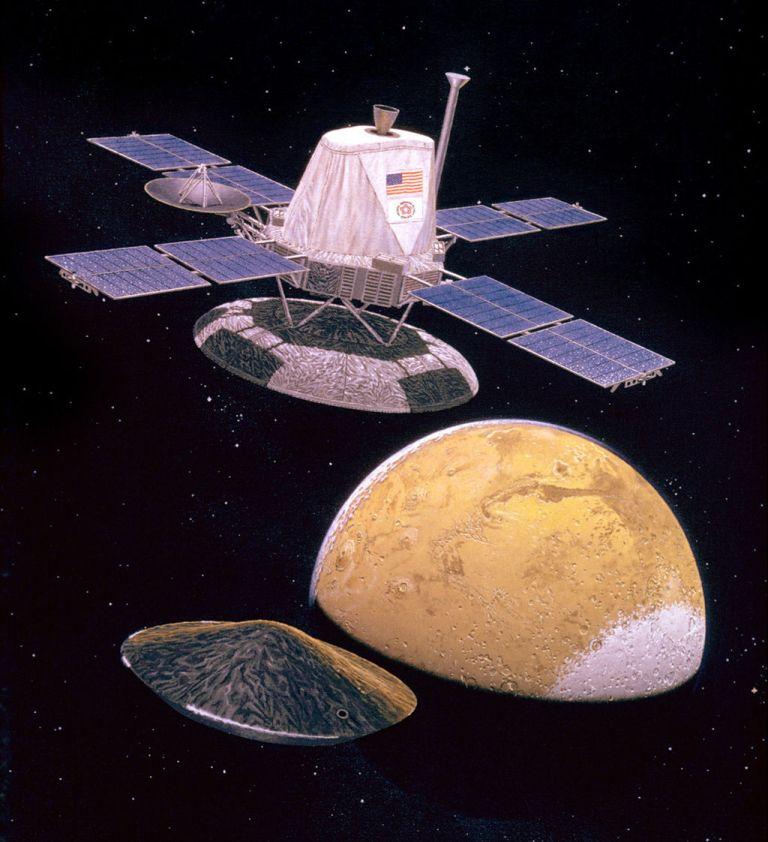
Viking 1 & Viking 2 were a pair of spacecraft as part of the Mars Viking Program. Each spacecraft was composed of an orbiter & lander. The two spacecraft were launched only 20 days apart, instructed to image the Red Planet in high resolution along with studying the planet’s atmosphere and surface. When Viking 1 touched down, it became the first to do so in Mars’ history!

Fast Summary Facts About Viking 1 & 2
- Type: Lander & Orbiter
- Destination: Planet Mars
- Status: Deactivated
- Launch Weight: 3,527 kgs (7,776 lbs)
- Launch Rocket: Titan III
- Launch Location: Cape Canaveral, Florida
- Viking 1
- Launch Date: August 20th 1975
- Landing Date: July 20th 1976
- Viking 2
- Launch Date: September 9th 1975
- Landing Date: September 3rd 1976
Facts About The Viking 1 Orbiter/Lander Mission!
- Viking 1 composed of an orbiter and lander which both orbited Mars while a target landing zone was selected.
- The Viking orbiters were based on the Mariner spacecraft design.
- Both Viking orbiters were powered by large solar panels. These provided 620 W of power for their camera’s and radio equipment to communicate with Earth!
- The images returned from the Viking orbiters revolutionized scientist’s view of how water had shaped the planet’s surface features.
- The Viking orbiter also took the first close up images of Phobos, one of Mars small moons!
- The Viking 1 orbiter operated and imaged Mars for 5 years.
- The Viking landers had to survive a fiery entry through the atmosphere, before descending to the surface by parachute and an automated rocket burn.
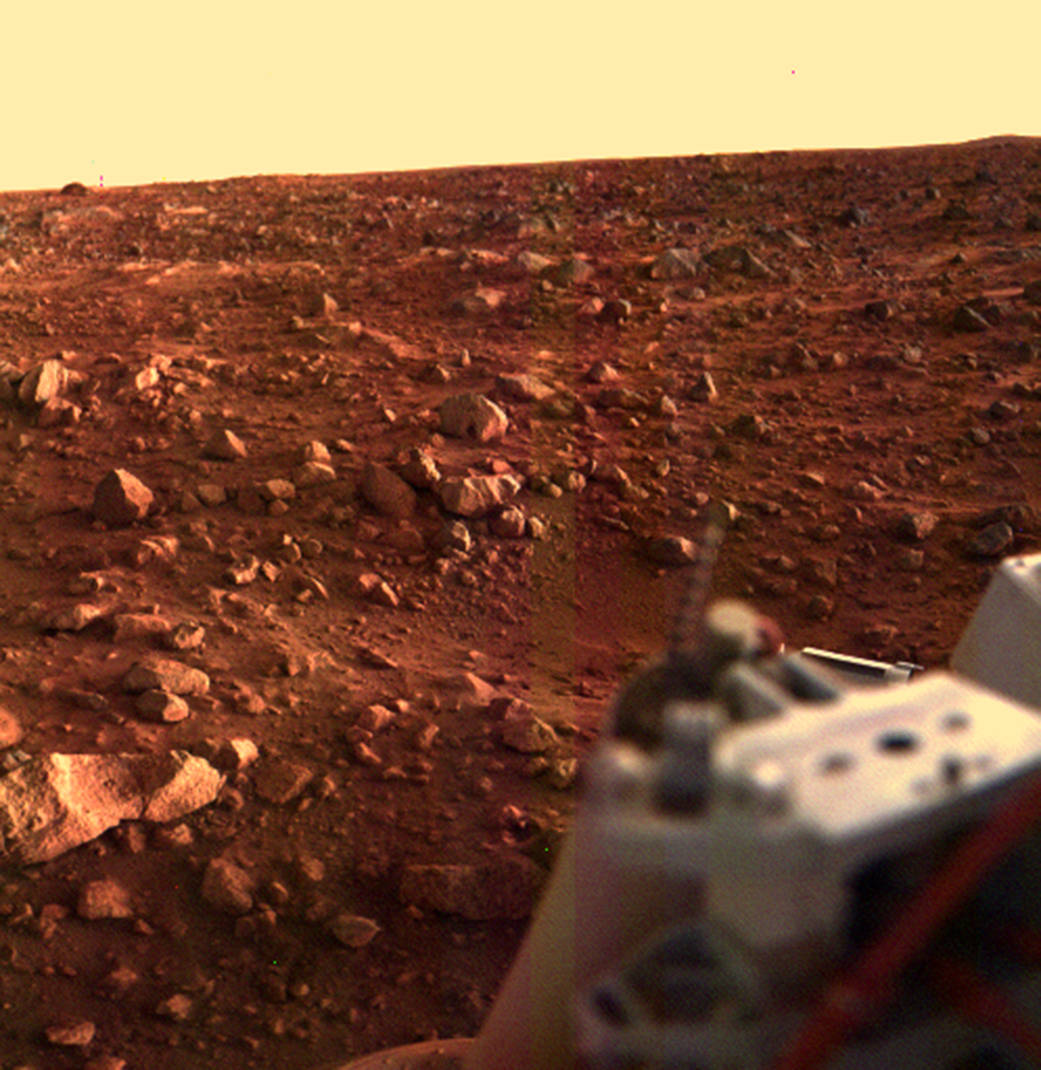
- On July 20, 1976, the Viking 1 lander became the first spacecraft to land successfully on Mars!
- It would also send the first images back to Earth from the surface of the Red Planet.
- The Viking 1 lander operated on the Martian surface for 2,307 days! A record it held until the rover Opportunity overtook it in 2010.
Interesting Fun Facts About The Viking 2 Mission!
- The Viking 2 orbiter returned more than 16,000 images and made over 700 orbits of Mars.
- The orbiter also took the first close up images of Deimos, one of Mars small moons!
- The orbiter was turned off after a leak in its liquid-fuelled propulsion system developed.
- It is not currently known whether the Viking 1 & 2 orbiters are still in orbit around Mars or have burnt-up and crashed on its surface.
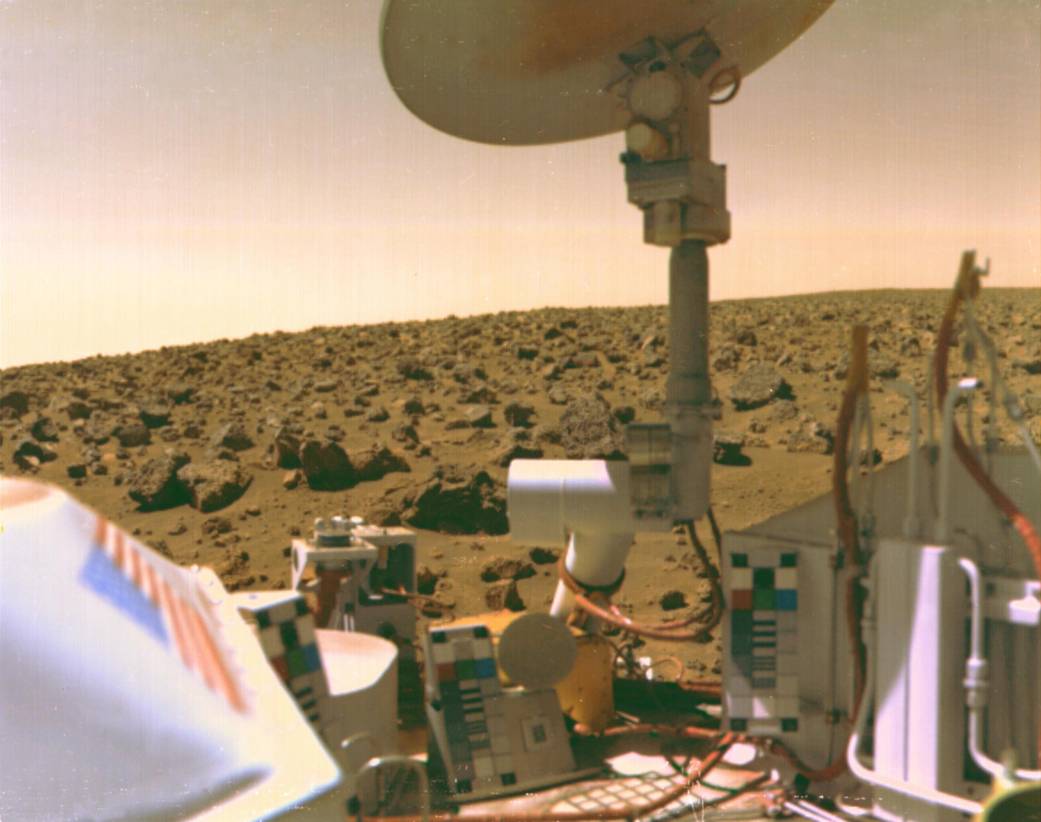
- Once on the surface, the Viking 2 lander had a mass of over 600 kgs (1320lbs)!
- It returned some iconic panoramic colour images of the red-tinged rock covered desert of Mars.
- The Viking landers attempted to search for signs of life. It was considered likely to exist in the Martian soil.
- Both Viking landers were powered by small radioisotope generators (also known as RTGs) – these are basically little nuclear power generators!
- The lander operated on the surface until April 11, 1980, when its batteries failed.
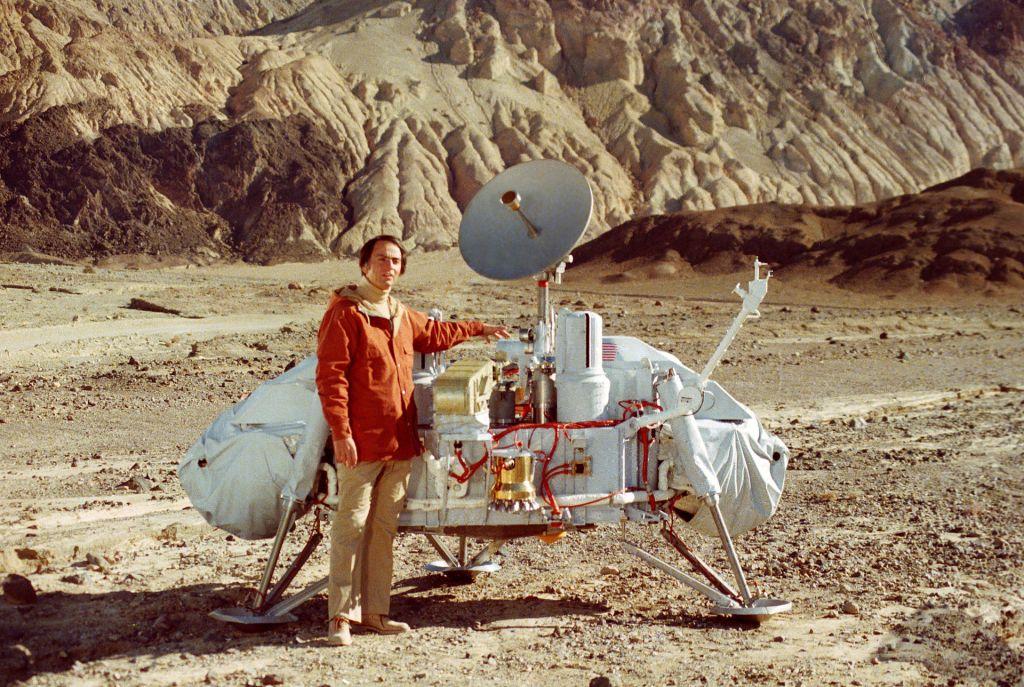
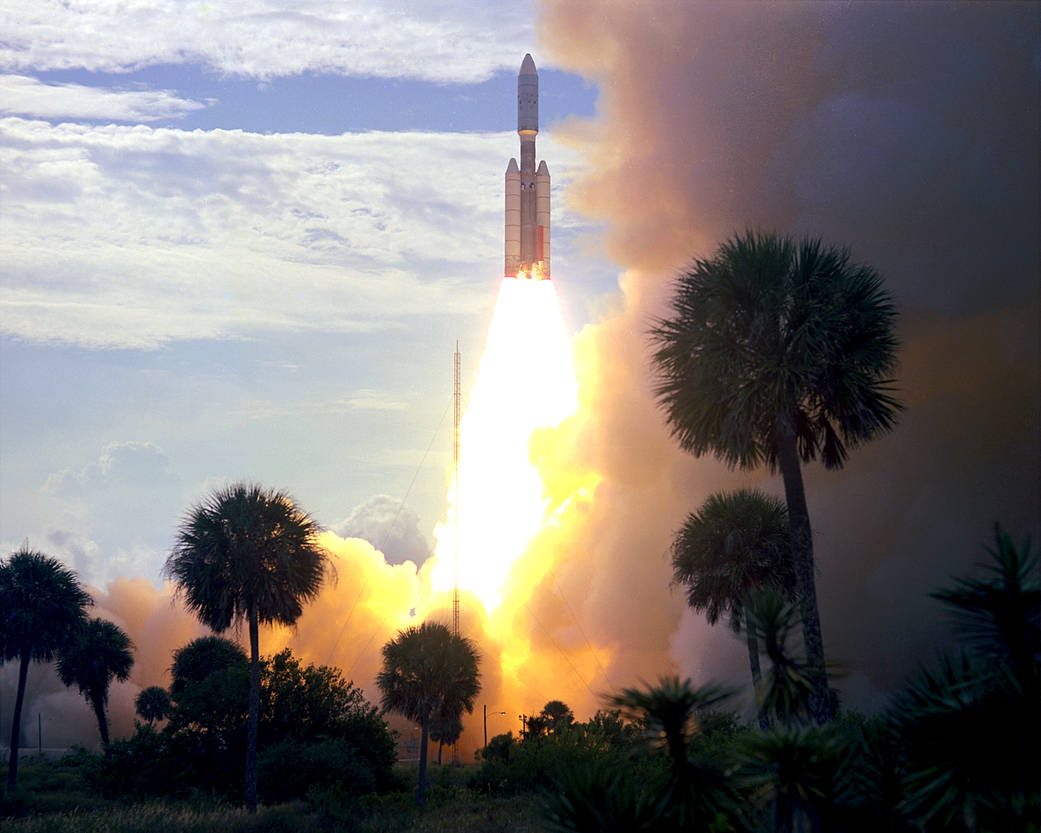
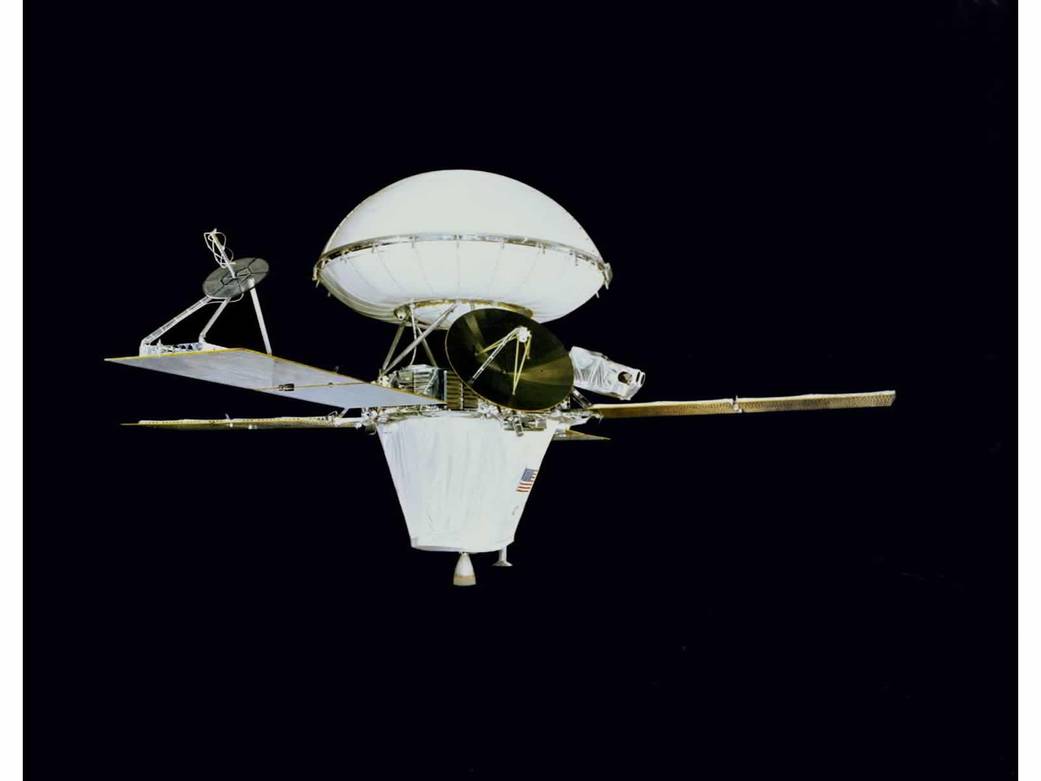
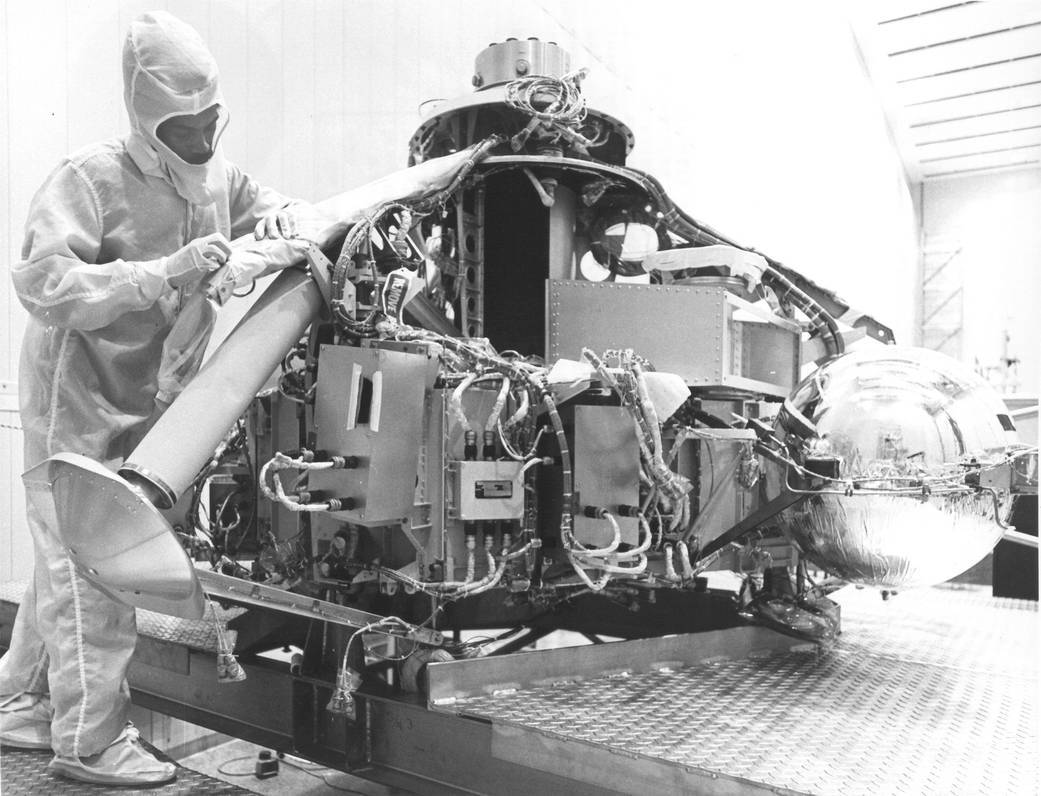






Viking 1 Development
Viking Model
Launch Vehicle
Viking 1 Spacecraft
Viking Spacecraft
Viking Lander 1
Viking 2 on Mars