Curiosity | Facts About NASA’s Nuclear Powered Mars Rover!
The Car-sized Explorer!
The Curiosity Rover is a car-sized robot sent to the Red Planet in 2011 to study the Martian climate and geology. The nuclear powered, 6-wheel rover landed on Mars in August 2012 utilizing an experimental ‘sky-crane’ system which softly lowered the rover into the Gale Crater landing zone. With an original mission length of 2 years, Curiosity has long since passed this and will continue to explore for years to come.
Curiosity’s Fast Summary Facts
- Type: Mars Rover
- Status: Ongoing
- Rover Mass: 899 kg (1,982 lbs)
- Launch Location: Cape Canaveral, Florida
- Launch Date: November 26th 2011
- Landing Date: August 6th 2012
- Distance Covered: 20+ km (12.4 miles)
- Mission Duration: 6 years+ and counting!
Interesting Fun Facts About The Curiosity Rover!
- As part of NASA’s exploration of Mars, the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) spacecraft (which includes the Curiosity Rover) was designed to determine whether Mars ever had the conditions to support microbial life.
- An Atlas V rocket, with extra solid rocket boosters (SRBs), was used to launch the MSL spacecraft towards Mars!
- The target landing zone for Curiosity was Gale Crater; the site of an ancient Martian lake. Here Curiosity could study Mars’ sedimentary rocks in the presence of liquid water to evaluate potential past habitability!
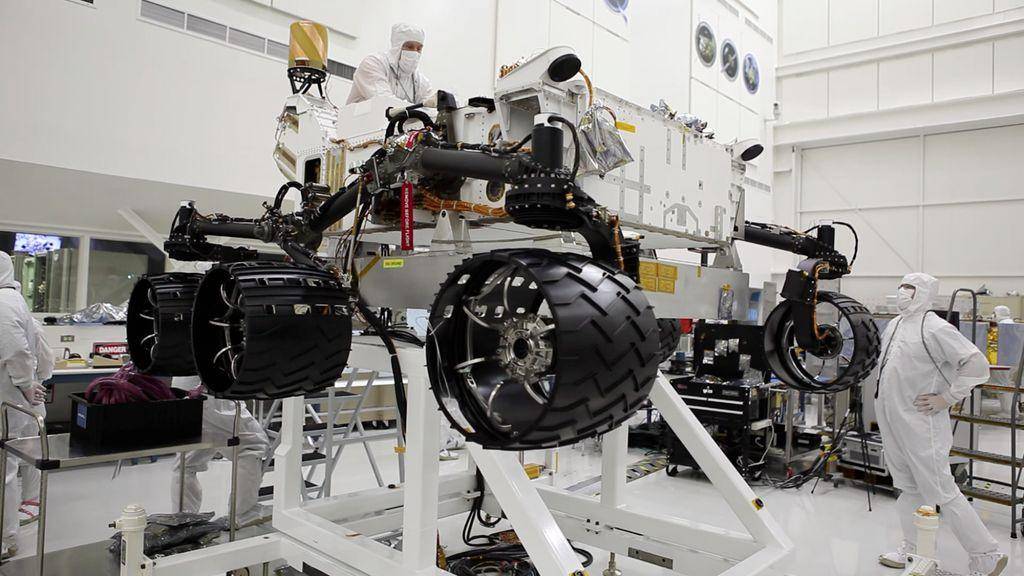
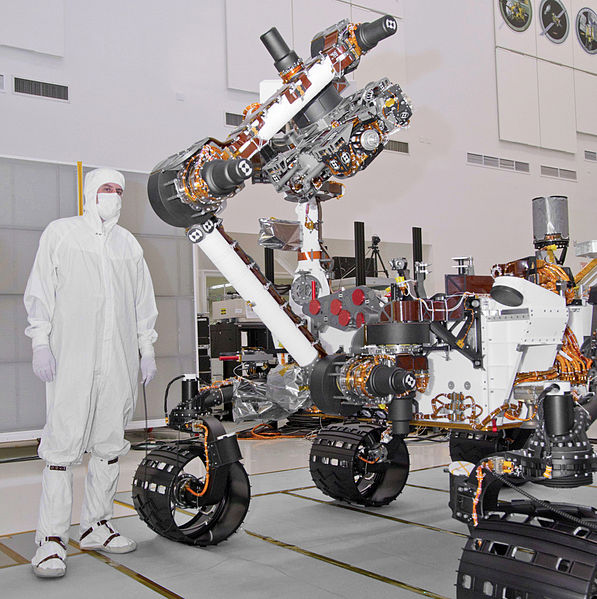
- The Curiosity Rover is huge compared to previous Martian rovers. It has a mass of 899 kg (1,982 lb) and measures 2.9 m (9.5 ft) long by 2.7 m (8.9 ft) wide and 2.2 m (7.2 ft) high. It is quite literally the size of a small car!
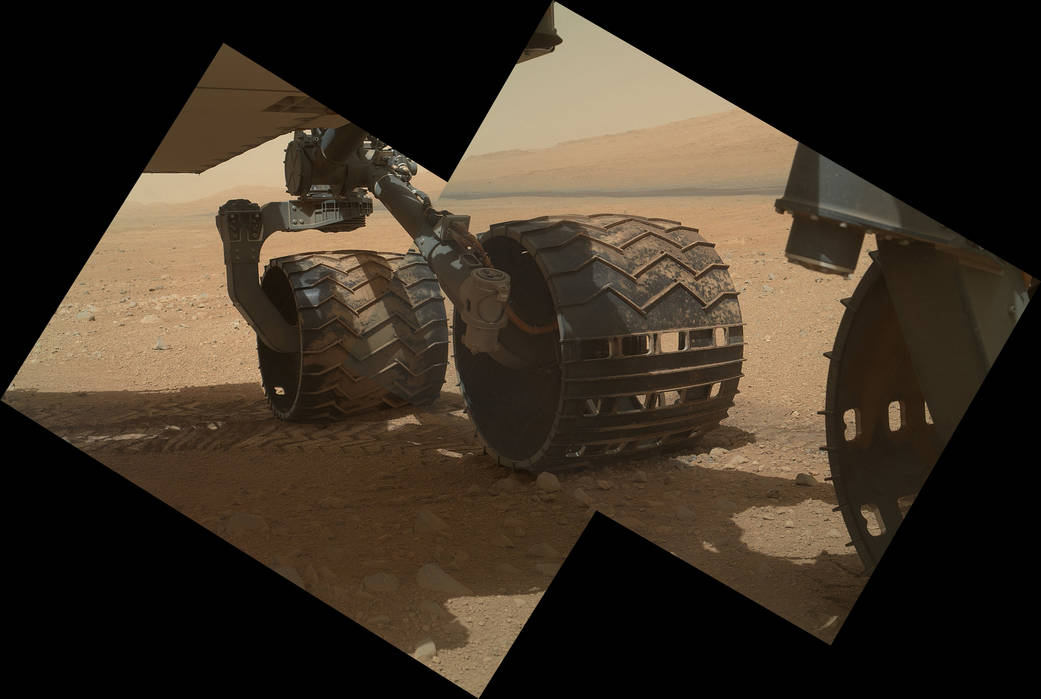
- The rover also has a 2.1 m (6.9 ft) long robotic arm which holds five of its scientific instruments.
- There is a total of 80 kg (180 lbs) of scientific instruments aboard Curiosity for analysing rock samples, monitoring the climate/environment and includes 17 cameras!
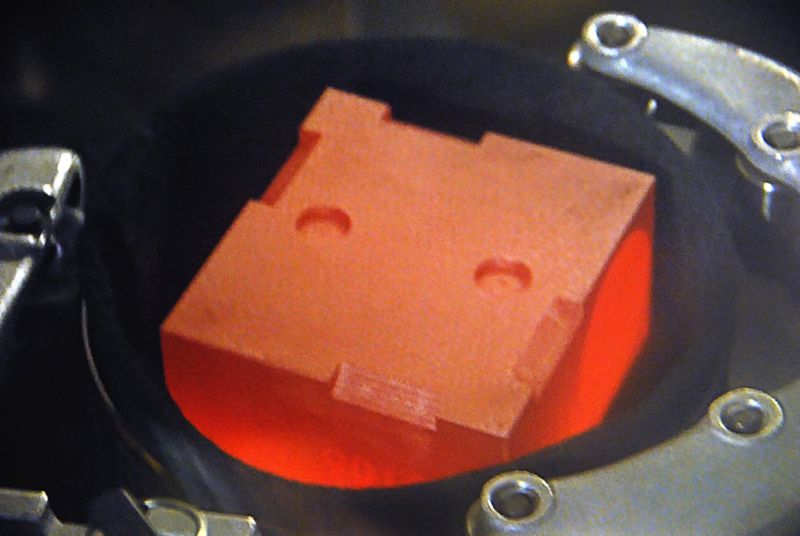
- Unlike the smaller rovers Spirit and Opportunity, Curiosity is powered by a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG), similar to the Viking Mars landers.
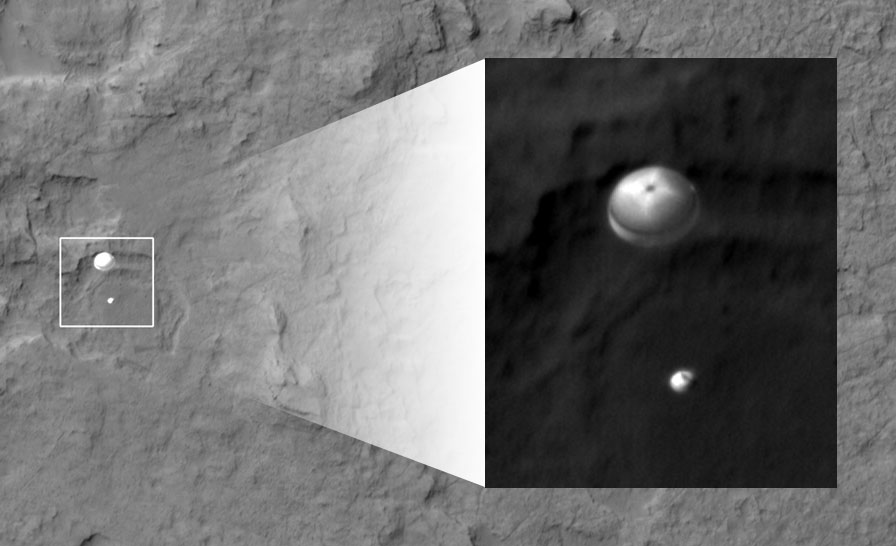
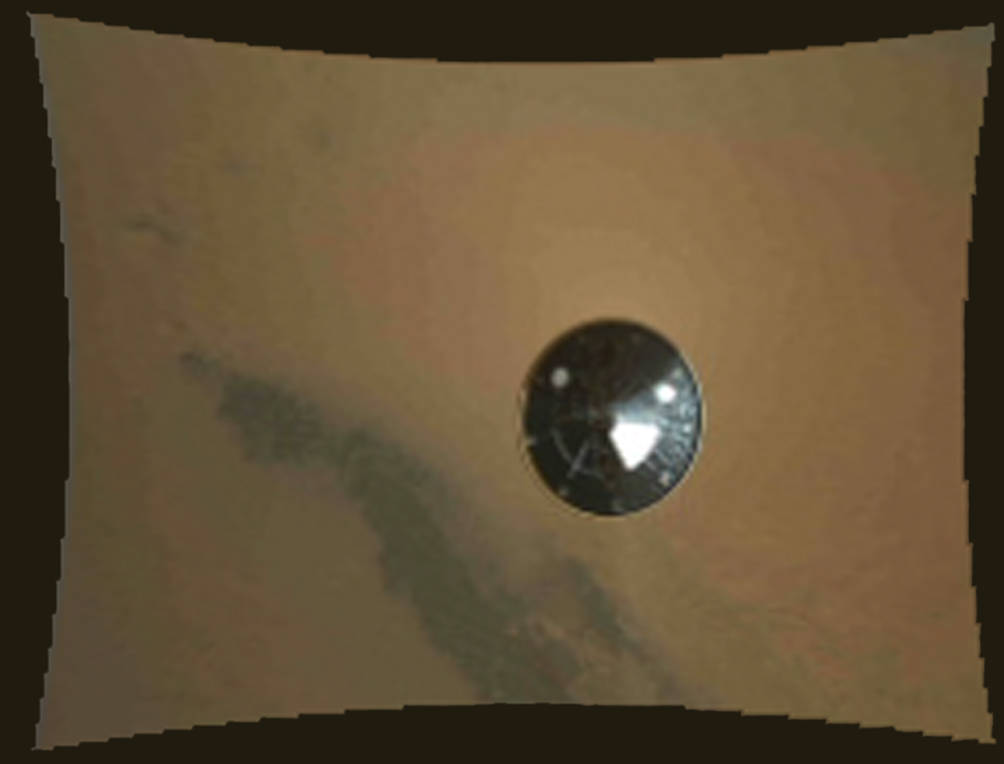
- After Curiosity’s fiery entry through Mars’ atmosphere, the rover was softly lowered to the surface (by cables) by a rocket-powered ‘sky-crane’. You can view a super cool animation of Curiosity’s landing here called the ‘Seven Minutes of Terror’!
- Curiosity landed less than 2.4 kilometres from the centre of its intended landing zone after a journey of over 560 million kilometres (350 million miles) from Earth!
- After one Martian year (687 Earth days), Curiosity had discovered enough evidence that Mars once had an environment favourable for microbial life! Even though this was likely billions of years ago...
- NASA has also determined that based on the radiation levels measured by Curiosity, that a safe long-duration crewed Mars mission in the future is possible.
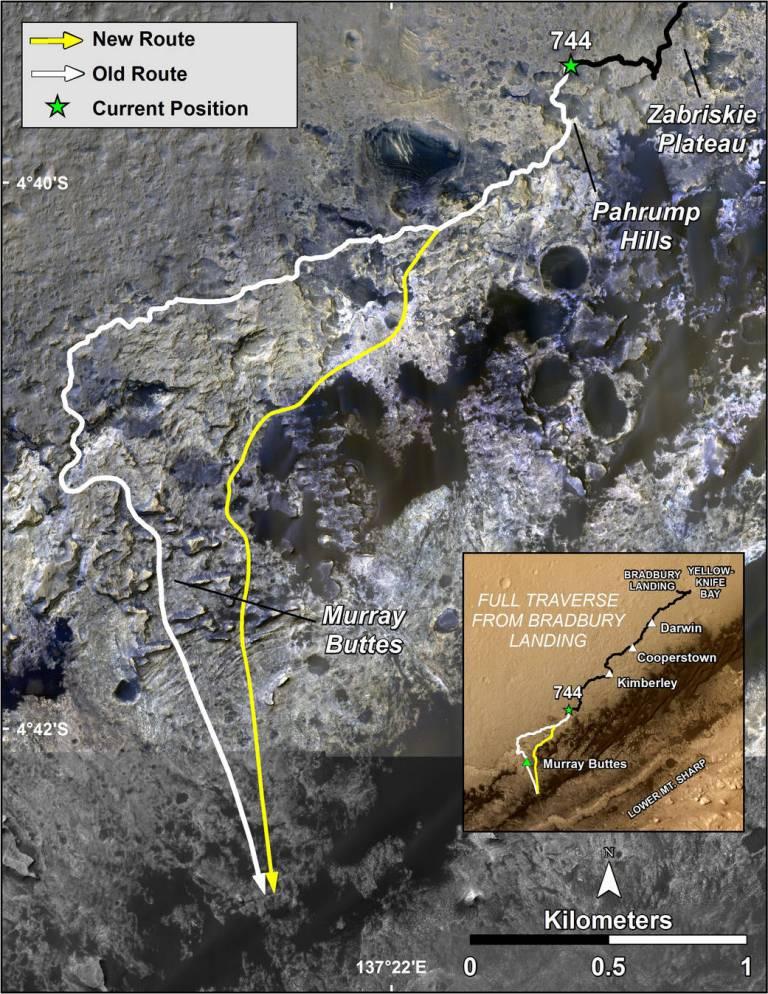
- The car-sized rover has now been exploring Gale Crater for over 5 years, covering more than 20 kilometres!
- NASA’s next-generation rover, the Mars 2020 Rover, will be based off Curiosity’s design and may soon join its big brother to continue our exploration of the Red Planet!
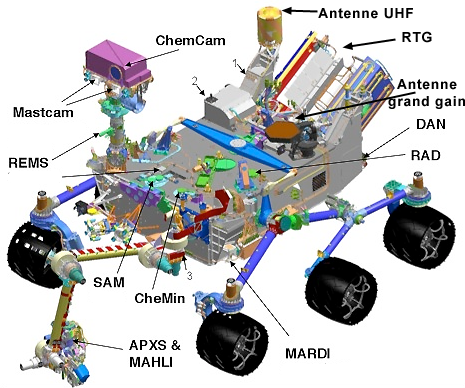








Mars Science Laboratory
Wheels Installed
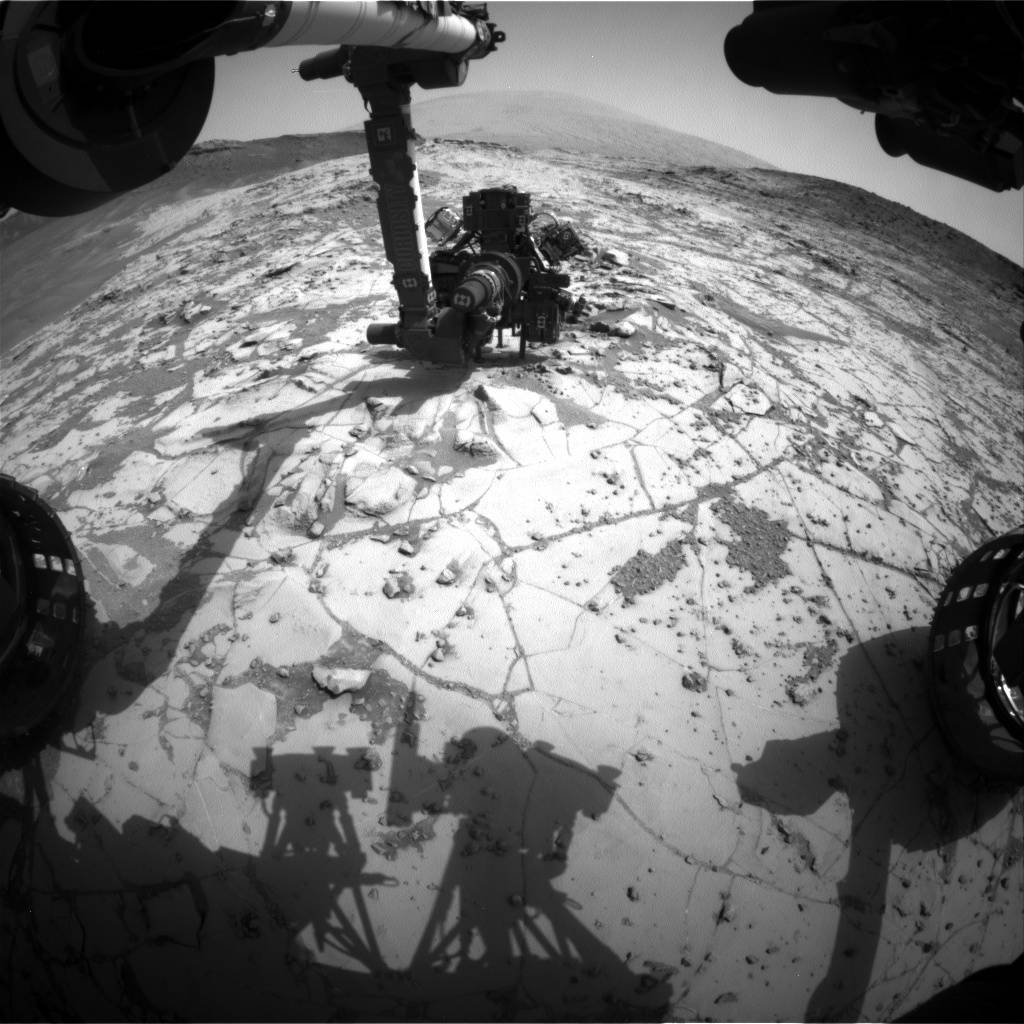
Curiosity's Arm
Curiosity Heat Shield
Descent of Curiosity
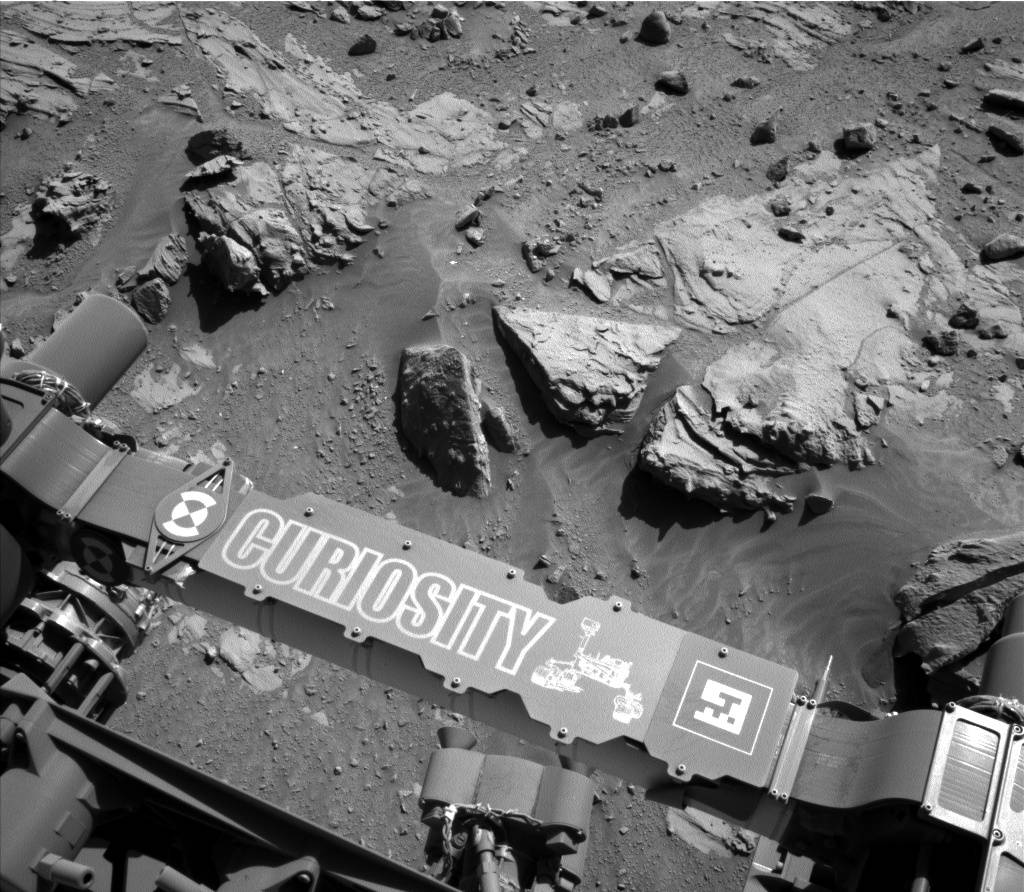
Curiosity Rover on Mars
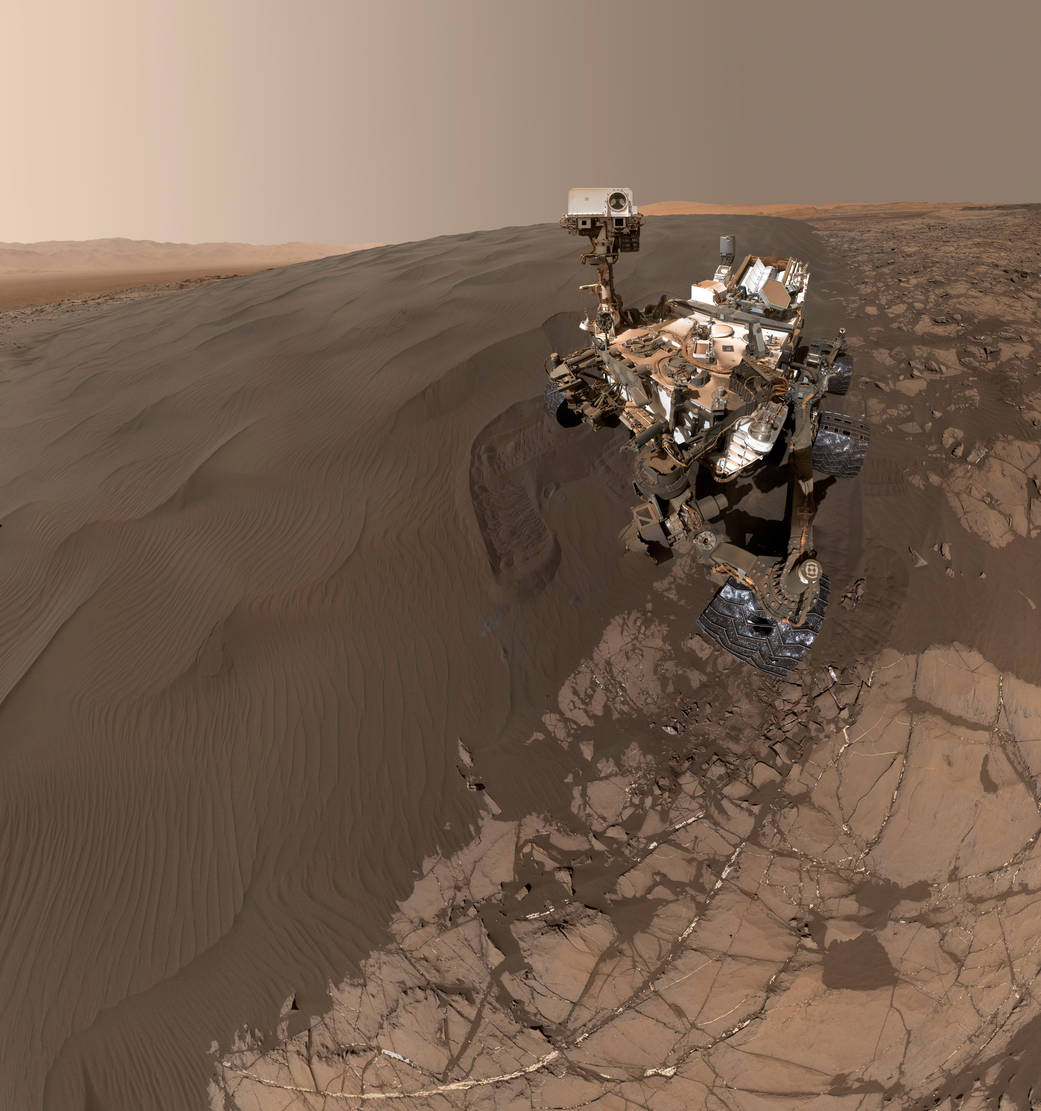
Curiosity at Namib Dune
Rare View
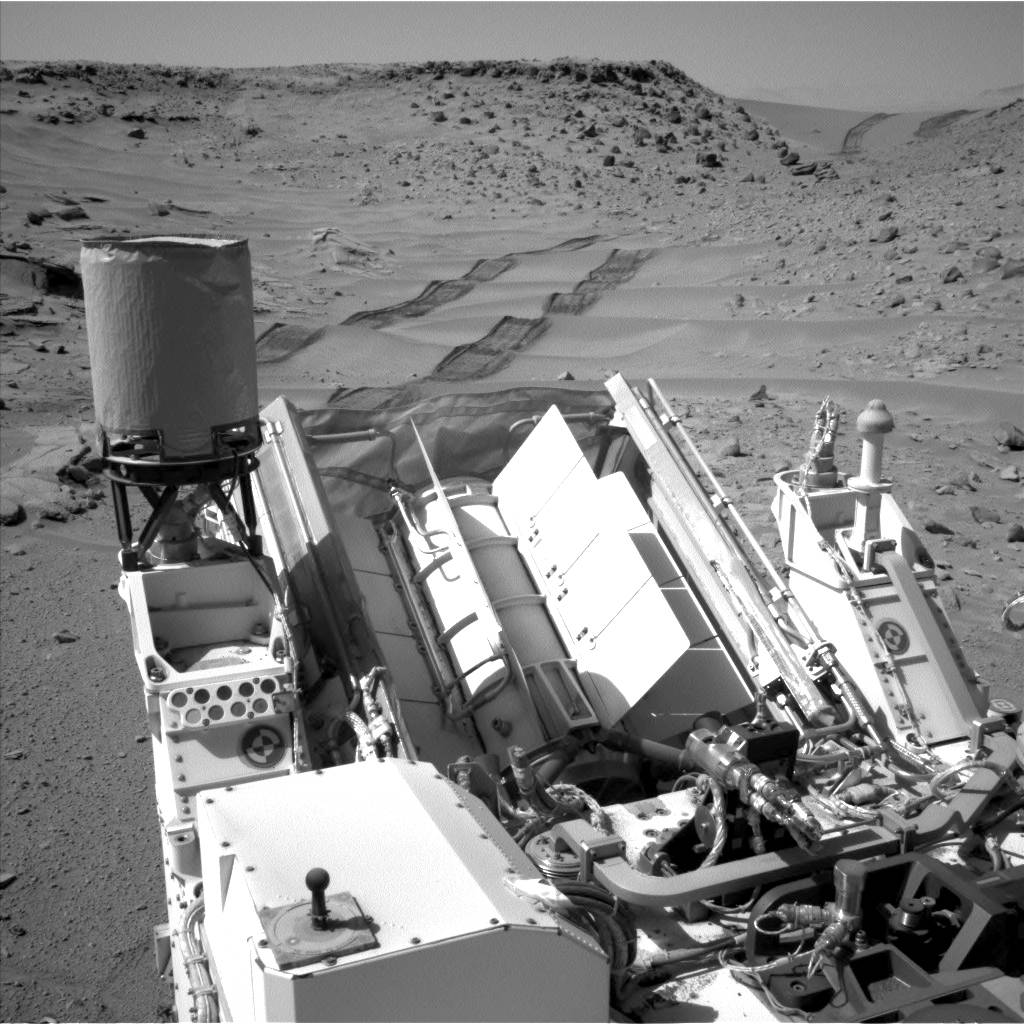
Power Source Fuel
Curiosity Mini-Drill Test
Wheels Inspection
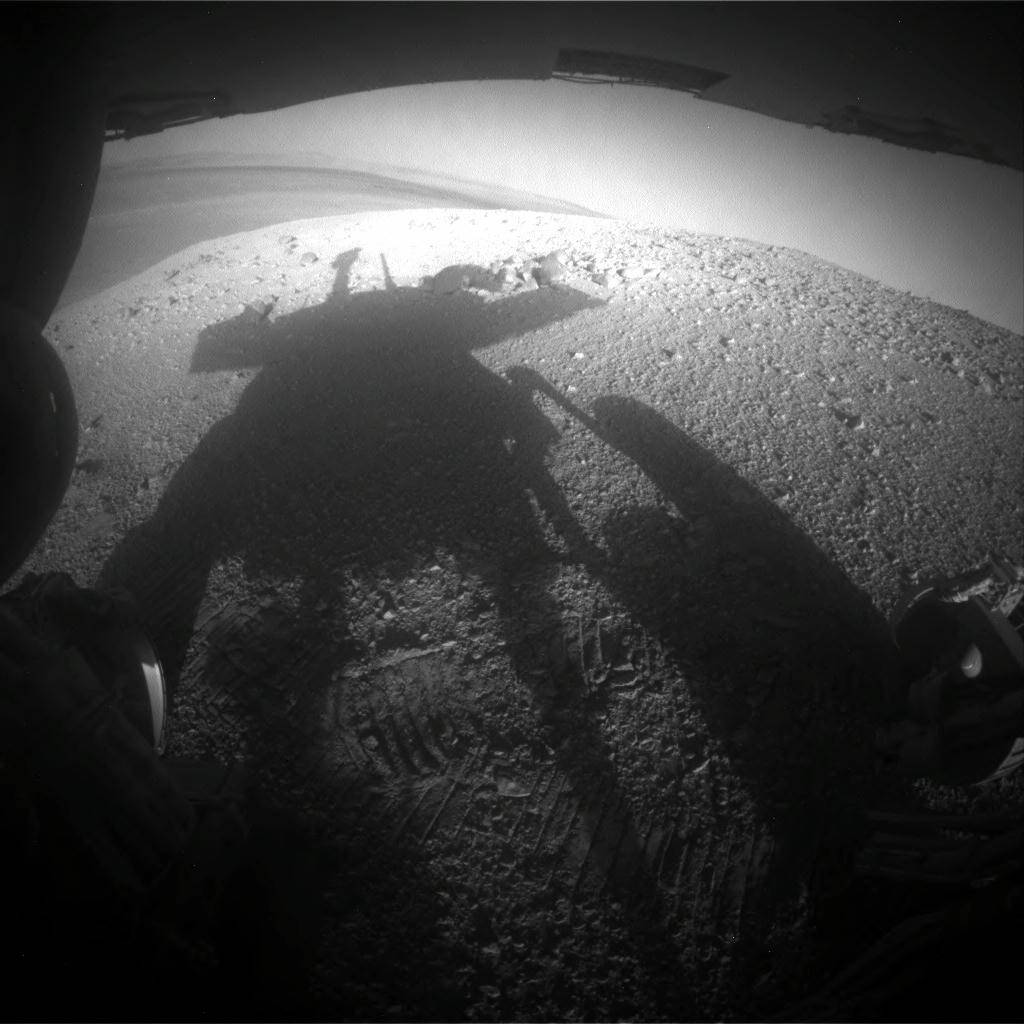
Shadow Portrait
Curiosity's Path
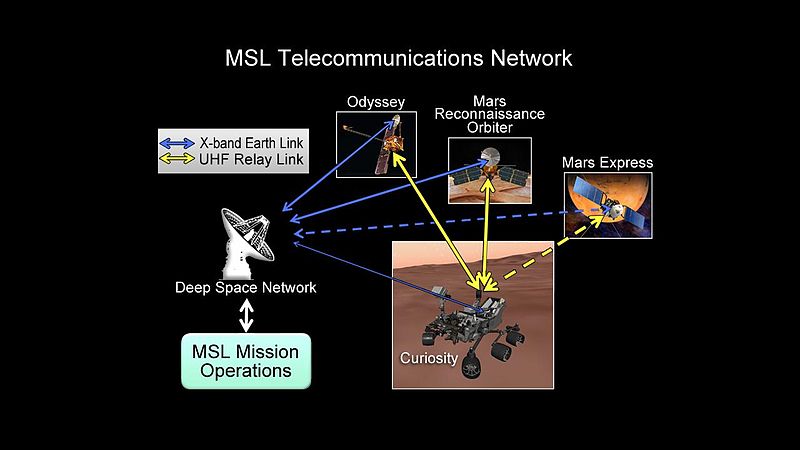
Curiosity Communication Network