Hubble Space Telescope | Revealing The Universe’s Hidden Treasures
Our Eye In Space
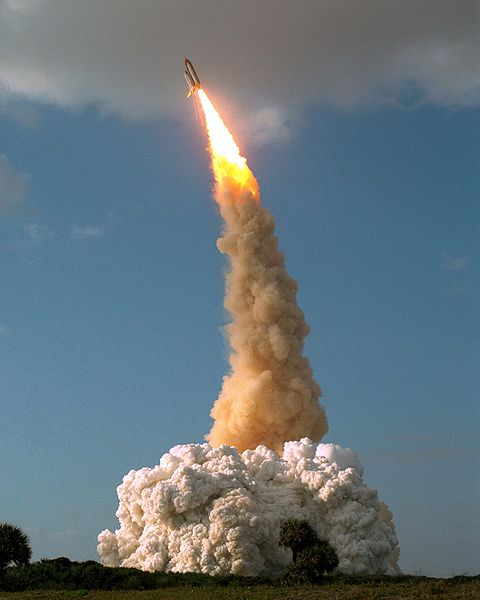
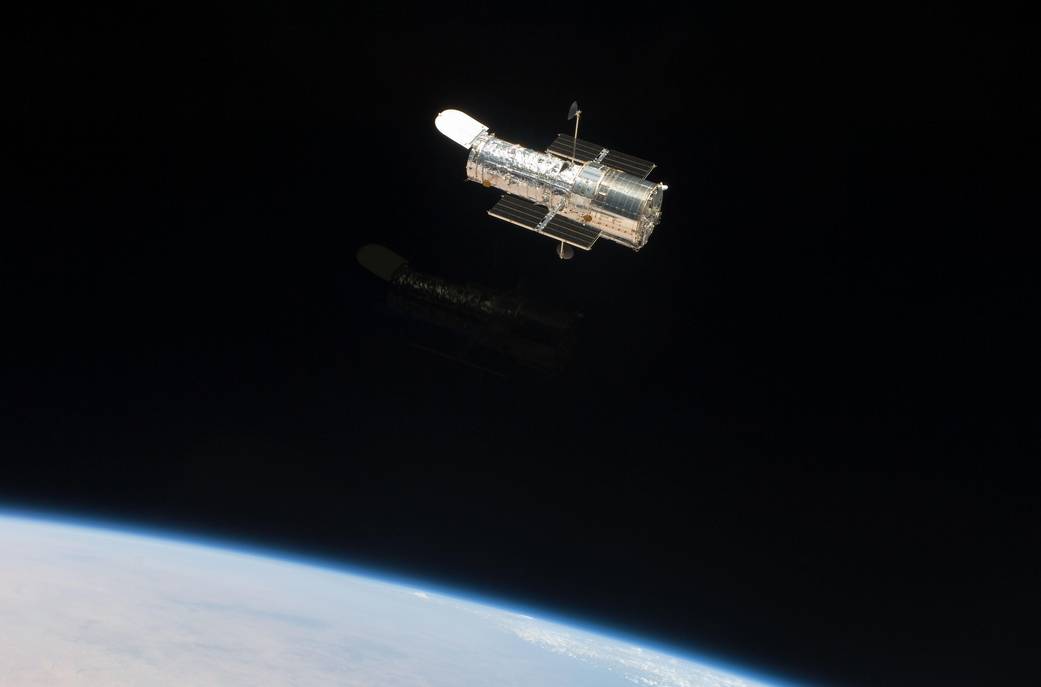
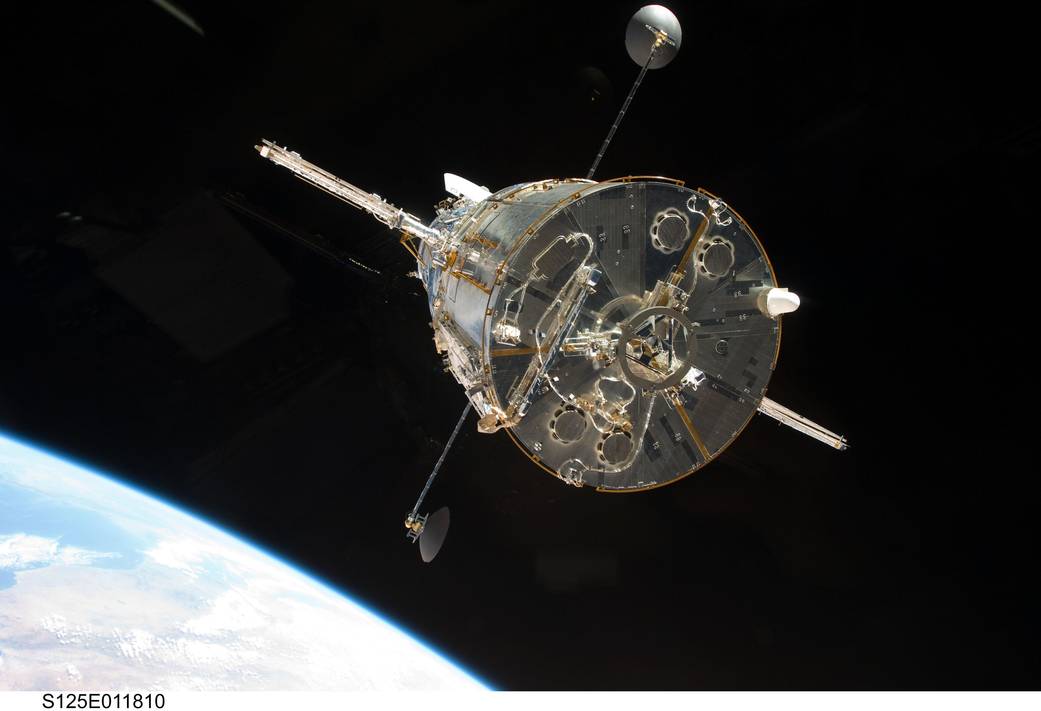
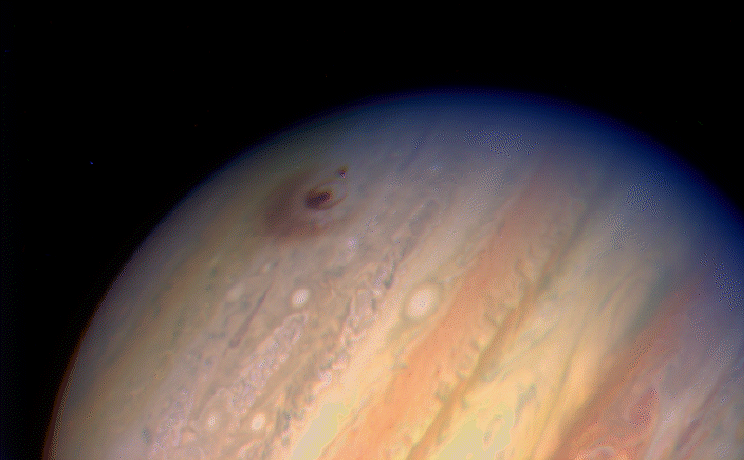
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is one of NASA ‘Great Observatories’ located in low Earth orbit. During its years of service, Hubble has made priceless discoveries in the field of astronomy while also ‘pulling back the curtain’ to reveal the true beauty of universe through countless stunning images. Hubble was launched by the Space Shuttle Discovery in 1990 for a planned mission of 5 years.
Hubble Space Telescope Fast Summary Facts!
- Type: Orbiting Space-Telescope
- Destination: Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Status: Active
- Launch Location: Kennedy Space Centre
- Launch Date: April 25th, 1990
- Mission Duration: Planned 5 years, currently 28+ years
Hubble And Its Importance
Until the year 1610, all that man knew about the night skies was what w could see with the naked eye. With the invention of the telescope came a revolution in astronomy. Our place in the cosmos would be forever changed as discoveries revealed the true nature of the Solar System, Milky Way Galaxy and universe beyond.
On Earth, telescopes would progressively get larger and larger. They would be located far from city lights, on mountain tops high above the atmosphere’s cloud. However, the ultimate location for a telescope is in space where it is free of the distorting effects of the Earth’s atmosphere.
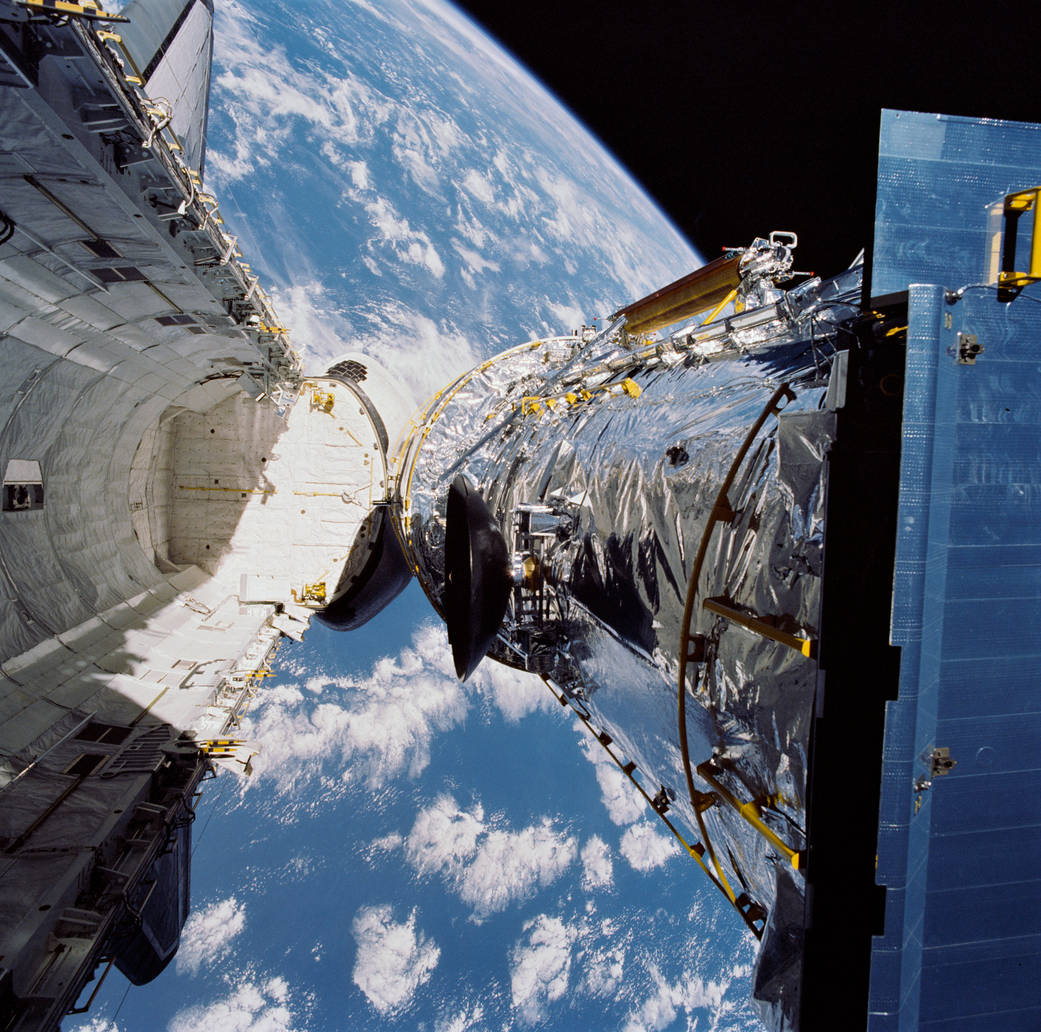
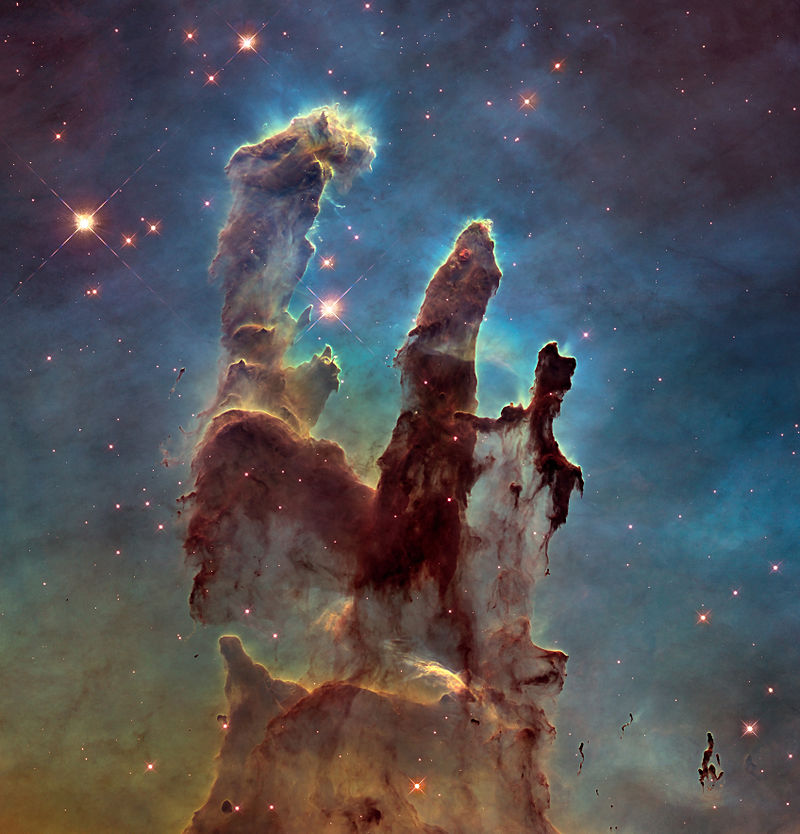
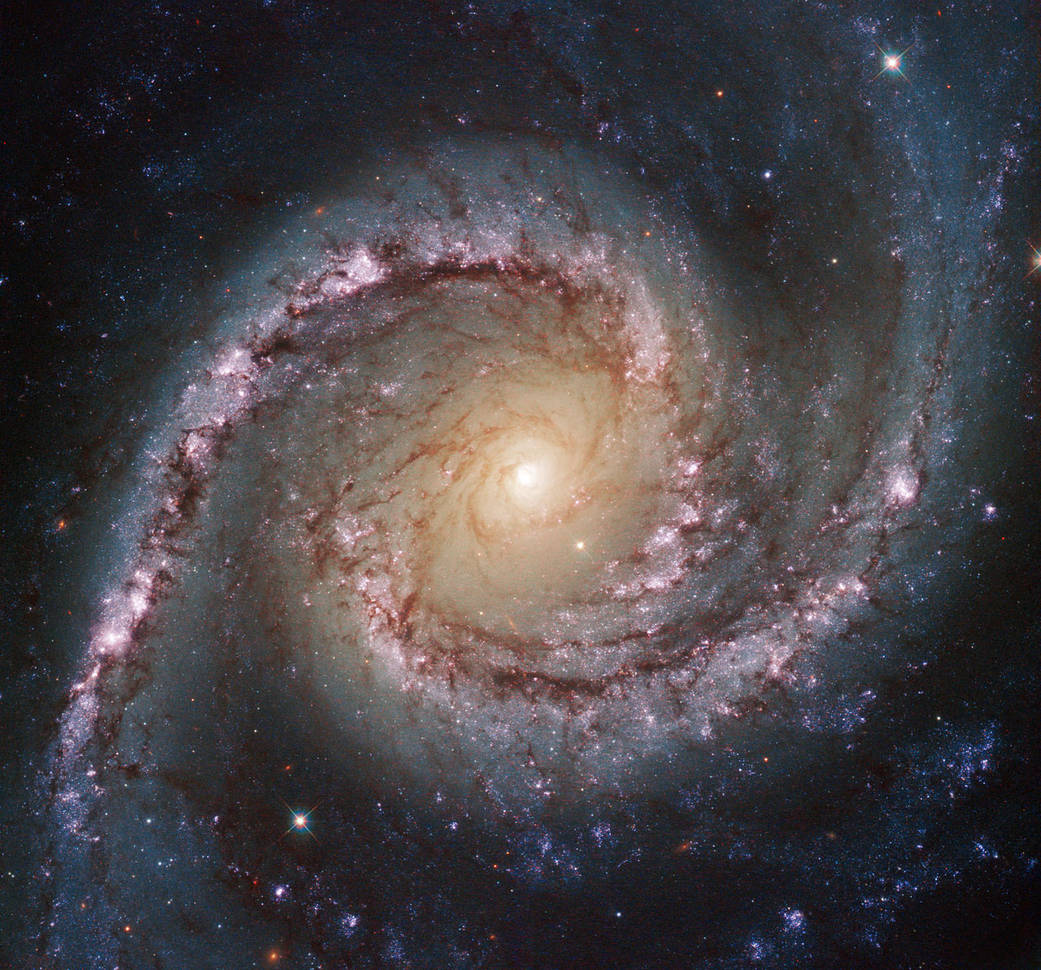
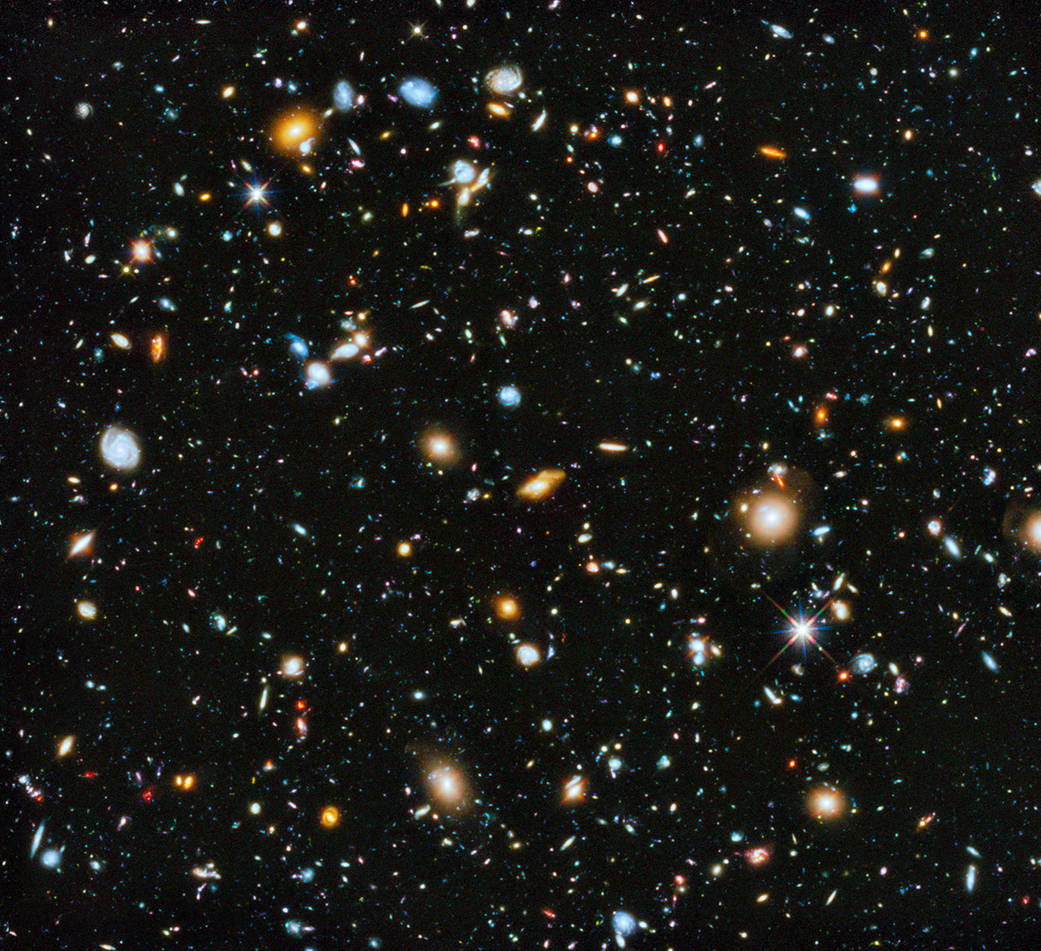
The Hubble Space Telescope was the first major telescope to be placed in space. Here Hubble conducts scientific observations and images distant faint objects in unprecedented detail. It would reveal objects of unimaginable beauty and increase our understanding of the Milky Way Galaxy, and the universe, more than any other instrument in history!
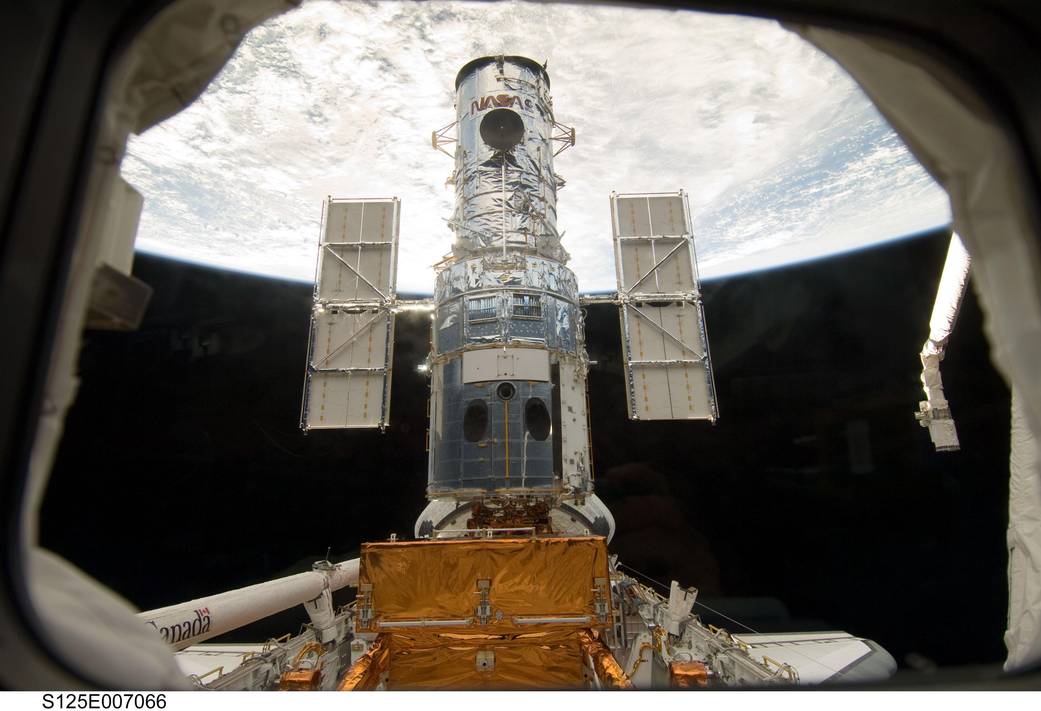
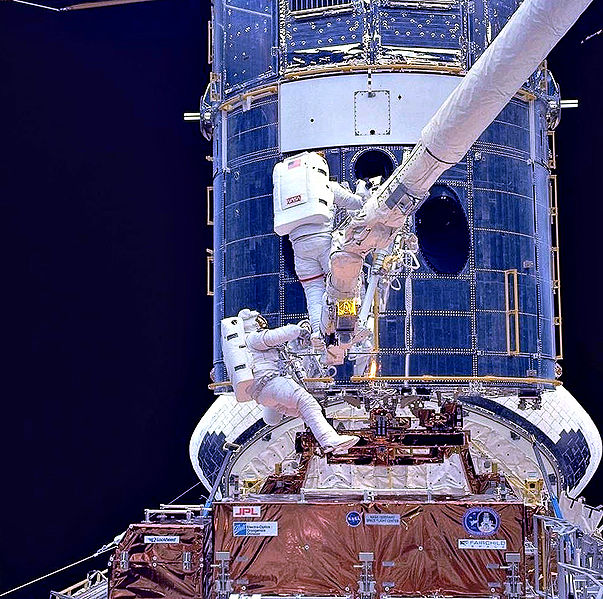
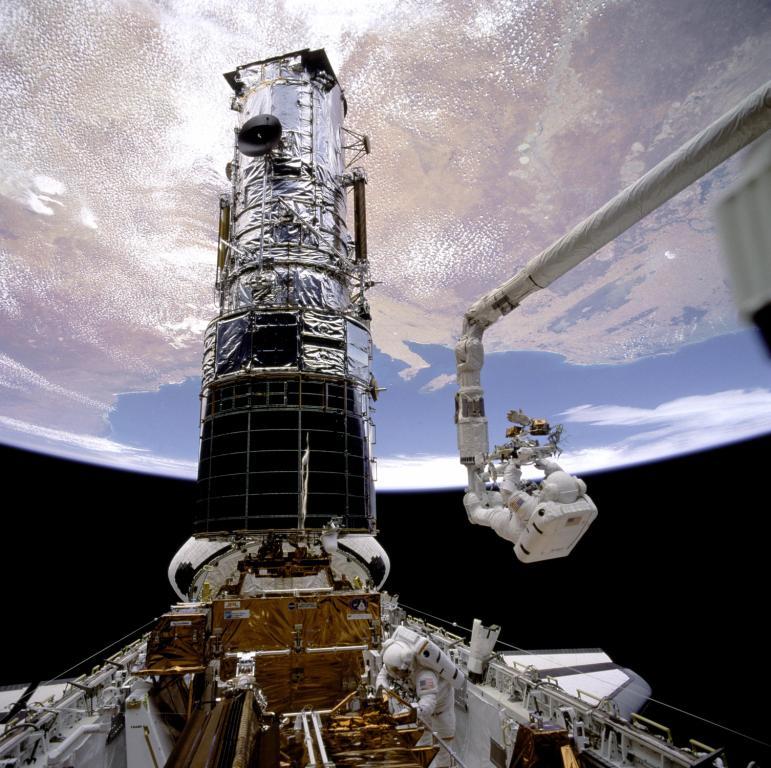
Since Hubble's launch in April 1990, there have been five further visits by Space Shuttle crews to service and upgrade one of NASA’s great observatories (along with the Chandra X-ray Observatory, the Spitzer Space Telescope and the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory). The first servicing was more of a ‘repair mission’ to correct for an error in Hubble’s primary mirror which resulted in blurry images!
Originally designed to last just 5 years, the HST is now approaching its 29th year of operation and may potentially last into the 2030’s. NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is planned as the successor to Hubble.
Quick Fun Facts About The Hubble Space Telescope!
- The HST was designed to observe in near ultraviolet, visible and near-infrared wavelengths
- The space-based telescope was named after the American astronomer Edwin Hubble who first discovered galaxies beyond the Milky Way Galaxy and that the universe is expanding at an increasing rate.
- The Space Shuttle Discovery carried Hubble into low earth orbit and it weighed over 11,100 kilograms (24,500 lbs) when launched.
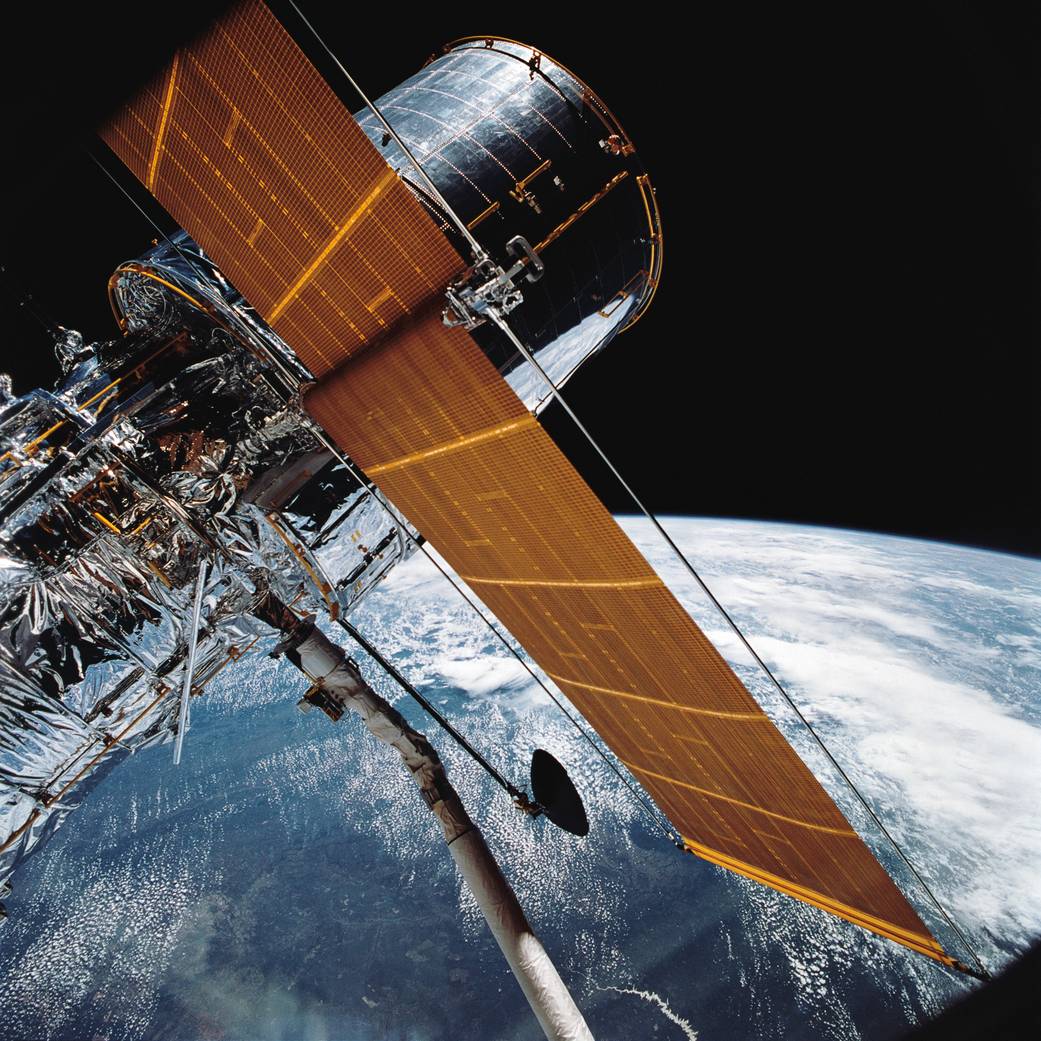
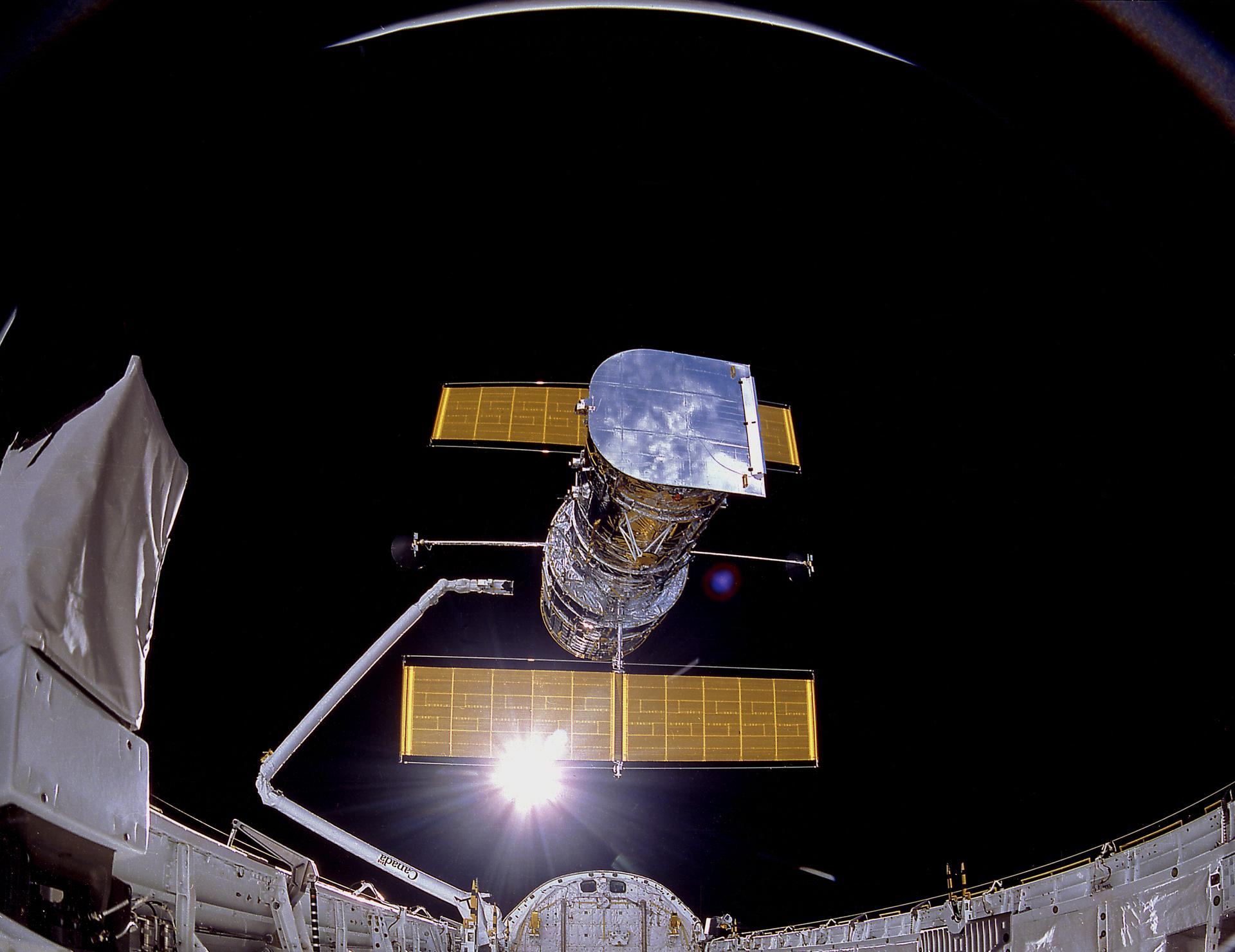
- Hubble is 13.2 m (43.5 ft) long and 4.3 m (13.8 ft) wide (larger than a large yellow school bus), so filled the whole Space Shuttle payload bay!
- When deployed, Hubble was put in a circular 615 km (382 miles) high orbit. Over the last 30 years, its orbit has decayed closer to 530 km (330 miles).
- Hubble whizzes around Earth at 27,300 kph (17,000 mph) and has covered over 6.5 billion km (4 billion miles).
- Hubble completes an orbit of Earth in only 95 minutes and has made over 150,000 of them since its launch in 1990!
- The telescope has made more than 1.3 million observations since its mission began!
- The HST doesn’t have any thrusters but turns and points by using small wheels powered by electricity from its solar panels.
- And Hubble’s mirror and instruments are so sensitive it can spot a torchlight on the surface of the Moon from the Earth!
- Hubble’s sensitive instruments mean it can observe very distant, dim and old objects. Some as old as 13.4 billion years old!
- So far Hubble’s cumulative costs are estimated to be close to USD $11 billion.