What Is The Global Positioning System (GPS)?
Locations With Military Precision!
Basically, the Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system comprised of at least 24 satellites. The U.S. Government built the system in the late 1970’s for military use but later allowed civilians to access and use the system. GPS works by providing information to a GPS receiver anywhere on Earth, in any weather, any time of day and all free of charge. The system requires signals from at least 3 satellites to calculate a location.
Quick Facts About The GPS Satellite Constellation!
- The first GPS satellites were launched by the U.S. Department of Defense (USDoD) in 1978 for use by the US military. The system was completed in 1995.
- In the early 1980s, limited civilian use was permitted, but the highest quality signal was reserved for military use and an intentionally degraded signal made available for civilians. Since the year 2000 this is no longer the case.
- The 2nd Space Operations Squadron of the U.S. Air Force maintains and operates the system from their control centre.
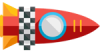
- The GPS constellation is comprised of at least 24 satellites for the system to be fully functional. Currently, there are 31 satellites on-orbit. These are arranged into six equally-spaced orbital planes.
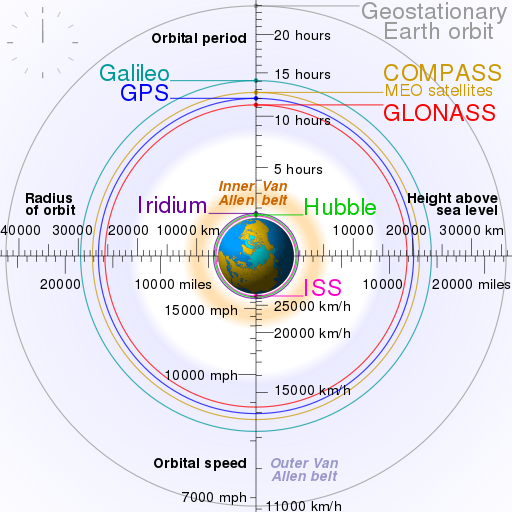
- The GPS satellites orbit the Earth in a medium Earth orbit (MEO) at an altitude of about 20,200 km (12,550 miles), far above the International Space Station (ISS) but below the geostationary satellites.
- The satellites orbit the Earth twice a day.
- A GPS satellite orbits at 14,000 km/h (8,700 mph) weighs approximately 910 kg (2,000 lbs) and is 5.2 metres wide.
- The satellites are powered by solar panels with their signal transmitter power only measuring 50 Watts - that's the same as a light bulb!
- The system works by transmitting a unique signal to a GPS receiver (such as your phone or navigation system) which allows it to calculate the location of the satellite. If the GPS device receives signals from 3 satellites it can calculate your 2D location on a map! If the device receives signals from 4 or more satellites it can calculate your 3D position!
- The number of satellites a GPS device receives depends on your location, whether you’re surrounded by obstacles and the time of day! A more accurate location is typically gained when you track more satellites.
- But GPS devices can calculate more than your location, they can also compute your speed, heading, track your path, distance travelled, the sunrise/sunset time and more!
- GPS devices are typically accurate down to 10 meters, but with additional correction equipment (used by rescue services for example) the accuracy can increase to below a meter!
- The U.S. Military isn’t the only operator of a space-based navigation system though, several other nations, or groups, operate or are constructing their own too;
- The Russian military operates a constellation called GLONASS
- The European Space Agency is building the Galileo satellite constellation
- China is also in the process of building their own system called BeiDou NSS
- With Japan and India also building systems.
- It is important for these nations to have their own independent systems so they are not reliant on America’s system for location services as the U.S. Military has the ability to selectively turn off the system to certain parts of the globe if they decide.
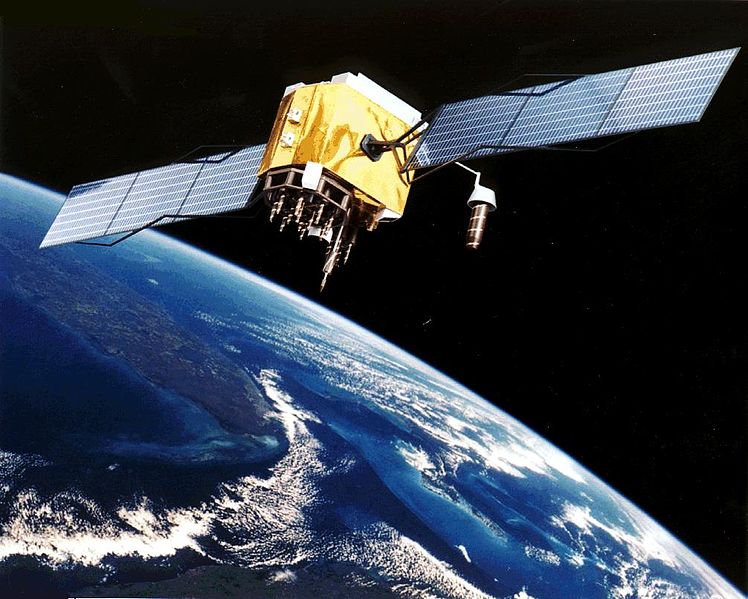
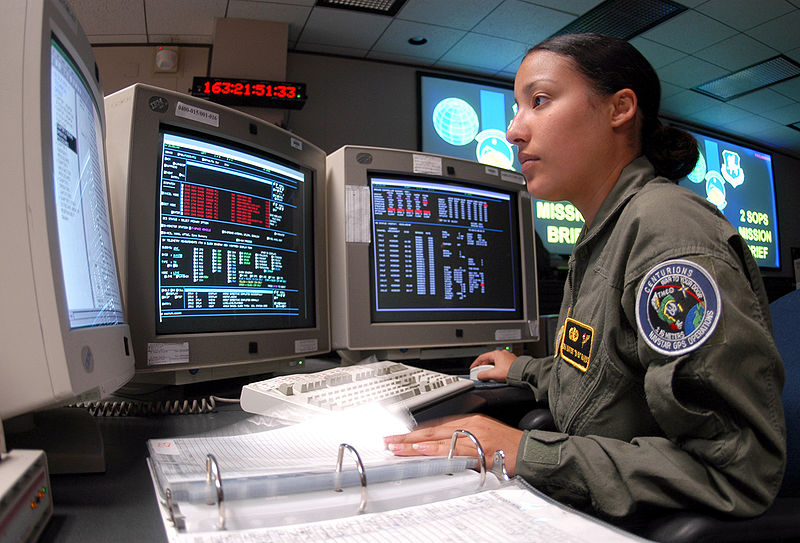


GPS Satellite
GPS Constellation
GPS Operator
Comparison Orbits