Tidal Forces 101 | Earth’s Tides & More Cool Effects!
Forces Of Attraction
A tidal force is the result of the gravitational interaction between two objects in space. Most commonly it is due to the difference in strength of gravity between a small and large body such as the Earth and the Moon. Tidal forces result in Earth’s daily tides, moons to be ‘tidally locked’, tidal acceleration and even the breakup of comets and the formation of planetary ring systems!
So What Exactly Are Tidal Forces?
A tidal force is the result of the non-uniform gravitational field between two objects, often of very different mass. This results in the side closest to the other body experiencing a stronger force of attraction than the far side, thus effectively stretching each body!
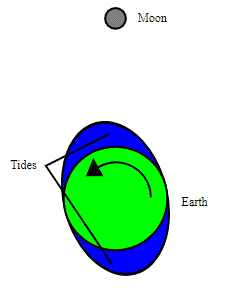
The Earth and Moon is the best example of this effect. The influence of the Moons gravity deforms Earth’s surface resulting in a slight bulge and the formation of our daily ocean tides! This same effect is also slowing Earth’s rotation very slightly, resulting in longer days!
Tidal forces don’t just form the Earth’s tides, they are also responsible for other phenomena too. These include tidal locking of moons, tidal acceleration, and the disintegration of moons or comets within the Roche limit, which can lead to the formation of ring systems.
Tidal Locking
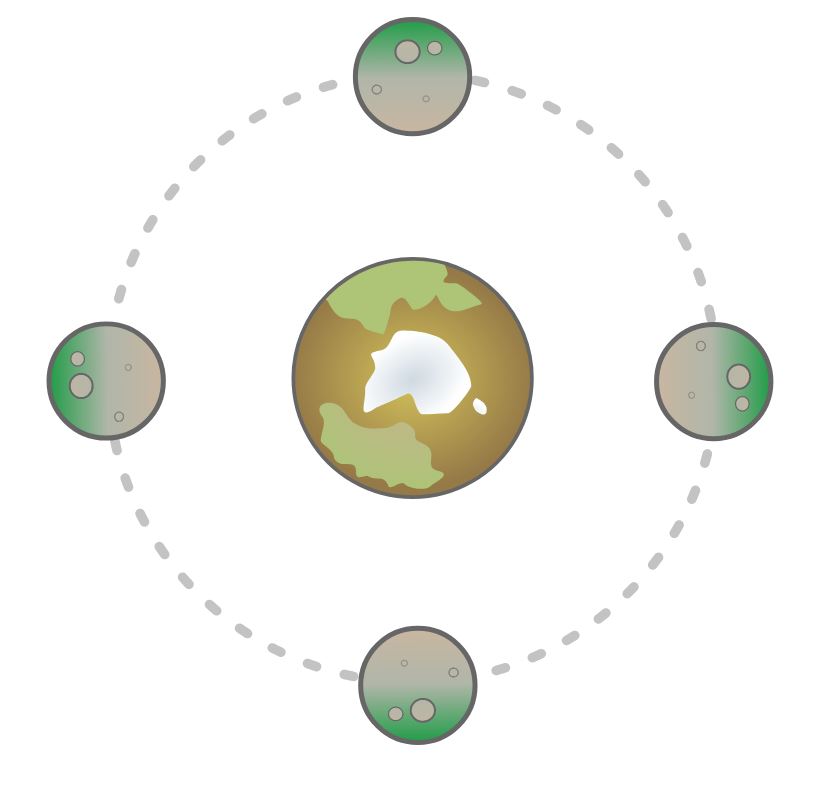
Tidal forces are responsible for the major moons of the solar system to be tidally locked to their planet. This means that the same side of the moon always faces the planet as it rotates on its axis, exactly once per orbit of the planet! This is why we can never see the far side of the Moon!
Tidal locking is caused by a moons rotational energy being lost (over a long period of time) as frictional heating due to the tidal forces and subsequent warping and squeezing. This loss of rotation energy stops once the moons rotational period matches its orbital period. This tidal heating from the gravitational warping of a moon produces dramatic volcanic effects on Jupiter's inner moon Io causing it to be the most volcanic body in the solar system!
Typically, only the moons become tidally locked and not the planets. However, if the distances are close and the difference in mass between the two bodies is close enough, they may both become tidally locked to each other over time. This is the case for the dwarf planet Pluto and its moon Charon.
Tidal Acceleration
Tidal acceleration occurs between a moon and a planet. Over time, tidal acceleration causes a moon to slowly move away if it is orbiting in the same direction as the planet's rotation. This also gradually slows the planet's rotation and lengthens its day. This is slowly happening between the Earth and Moon.
Tidal Deceleration
Tidal deceleration also occurs between a moon a larger body like a planet and results in the eventual breakup of the moon or impact with the planet’s surface.
There are two scenarios under which this occurs, first, when there is a fast orbiting inner moon, such as Phobos, which orbits Mars faster than the planet rotates. The tidal bulge Phobos raises on Mars acts to slow Phobos. Over millions of years, moons like Phobos will be slowed to the point where they will either strike the planet or cross within the planets ‘Roche limit’ and be tidally torn apart into fragments!
The other scenario where tidal deceleration causes a moon to breakup or be absorbed by the planet is where the moon orbits in a retrograde direction (i.e. opposite to the planets rotation). There is only one major moon in the solar system which orbits like this, that is Neptune's moon Triton. All the other retrograde moons orbit their planet at a great distance where the tidal forces are negligible.
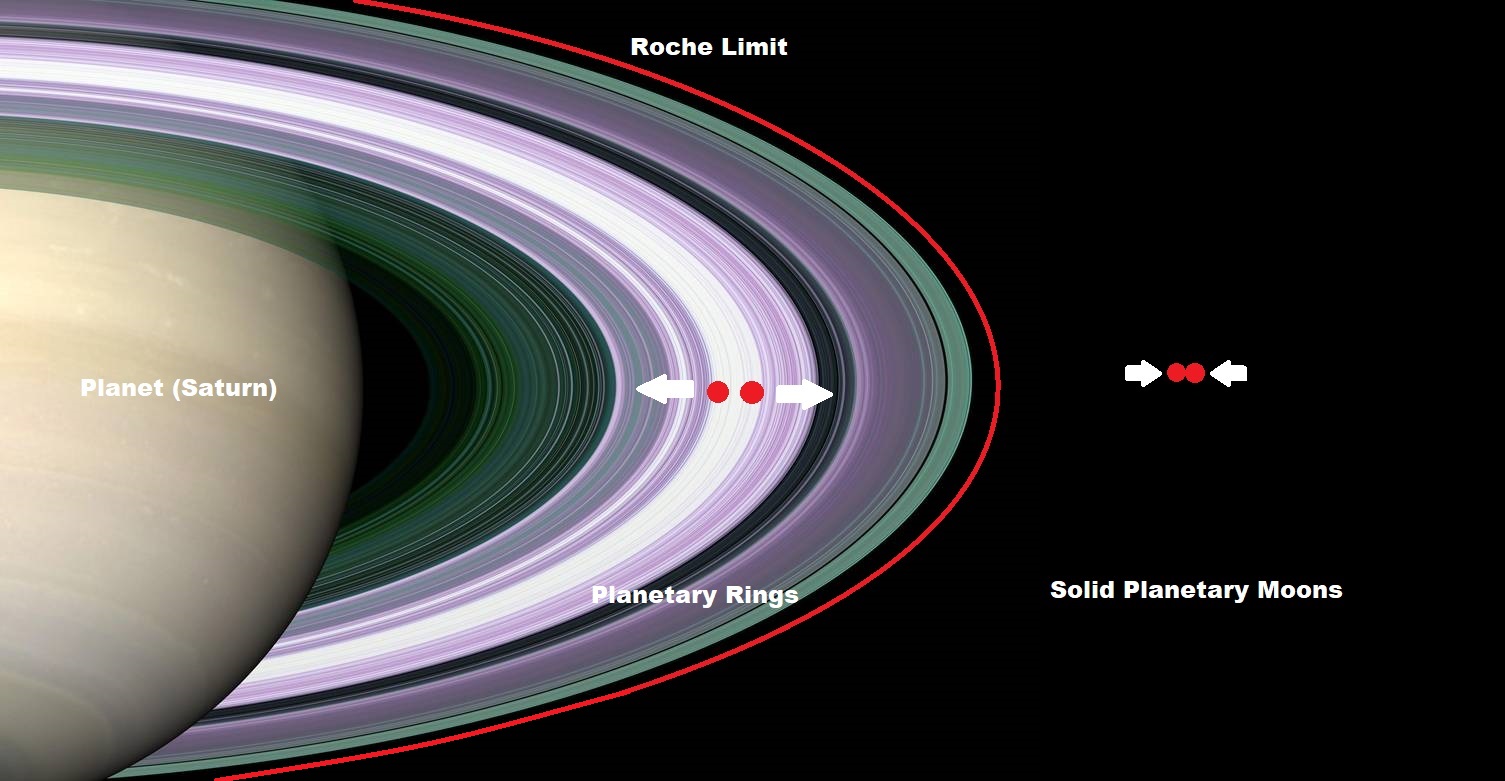
Destructive Power Of The Roche Limit
As an orbiting body gets closer to the larger body, such as a planet, the tidal forces increase. If the body crosses a point called the ‘Roche Limit’ the distorting tidal forces are so strong to cause an body (such as a moon or comet which strays too close) to disintegrate. This is because the warping and stretching force of the gravity gradient exceeds the body’s internal attraction.
This effect can be seen around Saturn where the tidal forces within the planets Roche Limit prevent the material in the rings from accreting into moons resulting in a planetary ring system. Tidal forces are also believed to have torn the comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 apart as it passed close to Jupiter in 1994.